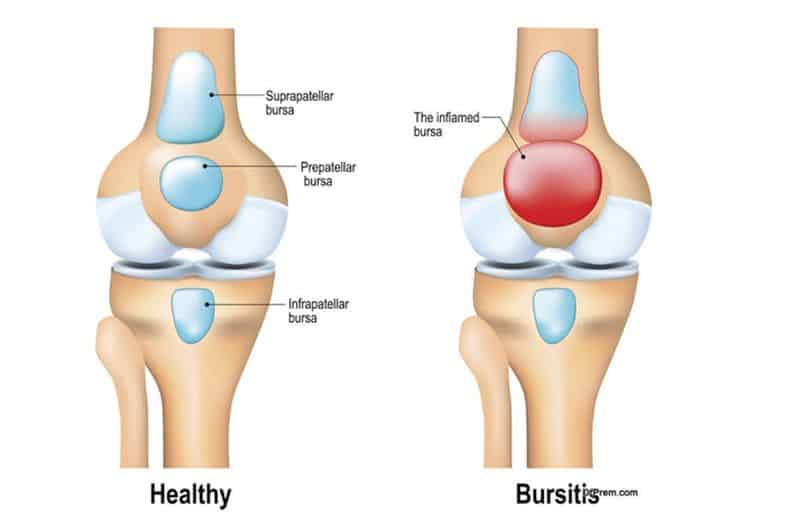
Bursitis: Alternative Medicine
Top Alternative Medicine
1. Dimethyl sulfoxide
Topical application of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to the affected area can provide relief from acute and chronic bursitis. DMSO rapidly penetrates the skin, alleviating the joint pain and swelling within a short period. The anti-inflammatory property of DMSO is comparable to that of aspirin. Apply 70 percent DMSO solution with cotton to the swollen areas, two to three times a day, for about three to six days. DMSO is considered safe when used for a few days. In some cases, applying the substance to the skin can cause dry skin, allergic reaction and stinging sensation. It is not recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women, diabetics and people with liver and kidney problems.
2. Movement therapy
Exercises that target the muscles around the joints reduce the stiffness and improve movement of the affected joint. The tension in the joints caused by the swollen bursa can be released with gently yoga poses, Tai Chi and Pilates.
3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture can be used as a safer alternative to conventional pain relief drugs. This traditional Chinese therapy can alleviate bursitis pain. Inserting fine needles in specific areas of the body induces secretion of adenosine, a chemical that is produced naturally by the body in response to pain.
4. Homeopathy
Homeopathy can be used for healing the symptoms of bursitis. Acute bursitis pain can be reduced with Arnica. Arnica gel can be applied topically to the affected area to reduce the swelling. Injury to the joint caused by repetitive movement usually subsides with Bellis perennis. Rhus toxicodendron and Ruta graveolons are common homeopathic medicines for treating bursitis.
5. Boswellia
6. Bromelain supplement
Bromelain is an enzyme isolated from the juice and stem of pineapple. Supplementation with bromelain helps to reduce inflammation of the joint affected by bursitis. It can also be used as a natural alternative to over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in decreasing pain in the joint. Although pineapple is a source of the anti-inflammatory chemical, pineapple fruit does not contain sufficient bromelain to provide relief from joint pain. Supplements containing 250 mg of bromelain is usually recommended for healing bursitis. Bromelain may delay blood clotting, especially in people on blood thinning medications. These supplements are not recommended for peptic ulcer patients.
7. Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps in repairing the injured connective tissues. It also acts as an antioxidant that can suppress inflammation triggered by the harmful activities of the free radicals. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of vitamin C supplements can be reinforced with added flavonoids. Consuming 250 to 3000 mg of supplements containing vitamin C and flavonoids can benefit people suffering from bursitis.
8. Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats with anti-inflammatory property. Fish oil, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, walnuts, canola oil and soybean oil are common dietary sources of omega-3 fats. The symptoms of bursitis might improve by taking about 1gm of omega-3 fatty acids two to three times daily. Supplements are usually safe when ingested in moderate doses. Intake of high doses of omega-3 fatty acids, more than 3 grams per day, might exacerbate the effect of blood thinning medications.
9. Glucosamine sulfate
Glucosamine sulfate is a chemical that occurs naturally in the fluid that lubricates the joint. By increasing the lubricating fluid level in the joint and strengthening the cartilage, supplementing with glucosamine sulfate helps to ease joint pain and inflammation. Usually, glucosamine sulfate is as effective as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in reducing pain triggered by chronic bursitis. People suffering from bursitis can take 500 mg of glucosamine sulfate supplement two to three times daily. Glucosamine sulfate is usually safe. Since the supplements are usually derived from shellfish, they are not recommended for people allergic to shellfish.