Applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine are creating a bigger impact on global healthcare by bridging the gap between the patient and the provider. It has the potential to improve productivity, efficiency, speed, accuracy and workflow of both the patients and physicians significantly.
Guide to Artificial Intelligence applications in global healthcare and its benefits in health management
-
Is everything good with AI applications in medicine?
-
How applications of Artificial intelligence in medicine are changing the conventional scenario?
-
Important applications of artificial intelligence in medical field
-
Data Management
-
Supportive tasks
-
Digital Consultation
-
Digital Nursing
-
Medication management
-
Diagnosing diseases
-
How machine learning is helping in diagnosis?
-
Advanced diagnosis in eye and colon diseases
-
Diagnosing colon polyps
-
Faster drug development
-
Stage 1: Identifying target molecules
-
Step 2: Discovering drug candidates
-
Step 3: Speeds up clinical trials
-
Step 4: Find biomarkers for diagnosis
-
AI alone creates a vaccine successfully
-
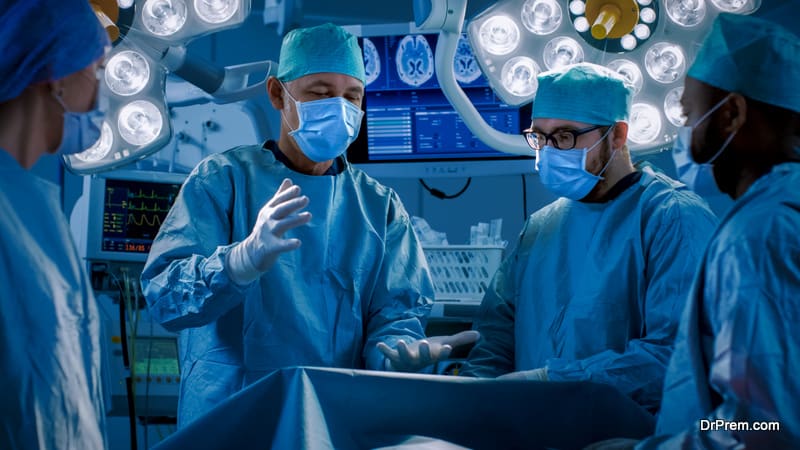
Enhanced robotic surgery
-
Aiding in personalized targeted treatment
-
Enhanced gene-editing
-
Personalized nutrition
-
Helping in treating anxiety and depression:
-
Freeing up doctor’s time
-
Evolution of medical practice with AI-assisted treatment management
-
Specialist diagnostic service in primary care:
-
Future applications
-
Key healthcare management benefits with AI
-
Keeping healthy
-
Early detection
-
Disease Management
-
Independence
-
Faster discovery
Is everything good with AI applications in medicine?
According to the recent declaration by CB Insights, the role of AI in healthcare is very crucial and hence is being used by almost about 86% healthcagenere service providers, biotechnology companies, and pharmaceutical companies. Experts have suggested that by the end of the year 2020, on an average, a burden of $54 million will be borne by these industries to ease the life of the common man.
This unique convergence of technology and medicine can help in streamlining tedious processes with more patient empowerment and substantial reduction in repetitive tasks. The standard medical practice in future would be like patients visiting a computer first before seeing the doctor. Events of misdiagnosis and medical errors would be a thing of past. Doctors can spend more quality time with patients bringing back the care in healthcare.
How applications of Artificial intelligence in medicine are changing the conventional scenario?
AI is a computer-based program that works with algorithms following specific rules, pattern matching, deep learning and cognitive computing. All these features help AI arrive at approximate conclusions without any human input. It is a man-made intelligence beyond the human brain that supports human intelligence.
The designing of AI matches the neural network of human brain. It teaches itself to read and interpret data by using several layers of non-linear processing units. It learns classifying data and making accurate predictions by scouring patient data from EHR (Electronic Health Records). The most striking feature of AI lies in data triage by picking the most important variables to predict health outcomes.
Besides this, AI also helps researchers in solving complex problems by quick meaningful interpretation of raw data, which can be applied in diagnosis, treatment and even predicting outcomes in medical treatments. There is hardly any area in healthcare where applications of AI will not fit suitably.
Important applications of artificial intelligence in medical field:
Data Management:
Artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine is widely used for compilation and further analysis of critical data generated in a hospital environment. The mentioned data is generated, collected, stored, reformatted and is being tracked whenever required for quick, relevant, and reliable access.
Supportive tasks:
Various repetitive jobs, such as X-Ray, CT scan, Test analysis etc. are being performed with the help of artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine. Specifically, cardiology and radiology are two of the most common disciplines wherein the AI has a crucial role in faster and accurate analysis.
Digital Consultation:
Nowadays, the patient does not have to travel all the way just for the consultation. Multiple apps have been developed to enable long distance communication between the doctor and the patient. One of them can be referred to be as Babylon that can be used to offer virtual medical consultation in the comfort of your home. With the help of artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine, virtual consultation with experts can be possible and have gained tremendous popularity.
Digital Nursing:
It is another interesting application of AI, wherein the patient’s condition is being monitored through an app – such as his/her blood pressure, sugar, heart rate, etc. The app can also indicate details about the patient’s medicines and can inform the patient when he/she has to take the medication. There are multiple specialty programmes, which can assist patients in case of a particular disease – same as the trained nurse.
Medication management:
The AI cure app has been recently developed by the National Institute of Health, which can continuously monitor the patient’s medication programme. This can be achieved by synchronizing the smart phone’s webcam with AI in order to make sure that the patients are taking the right medicine in a prescribed manner. Thus, this artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine has helped manage many patients their critical medical conditions.
Thus, with the development of AI in the healthcare system, the focus has been to decrease common issues that are currently present in the healthcare system and to be beneficial to patients in obtaining services within much lesser time span, at their comfort, and with minimum cost. Experts are acknowledging the AI to be highly beneficial in easing the life of a diseased and making him/her more independent.
Diagnosing diseases:
Accurate diagnosis of diseases demands years of experience. Advanced diagnostic tests available are arduous and time consuming – the demand often exceeding the supply. Global healthcare system is under severe stress due to this. Life-saving diagnostics are being delayed risking the patient’s lives.
How machine learning is helping in diagnosis?
Machine learning algorithms see the patterns of patient symptoms similarly as physicians do. But the difference is they need a huge number of data in hundreds and thousands to identify and categorize the pattern. All the data should be fed in the digitized format as machines are unable to read textbooks.
Therefore, deep-learning AI can diagnose:
- Lung cancer and strokes based on digitized CT scans
- Assess the risk associated with sudden cardiac arrest by studying electrocardiograms and cardiac MRI images
- Skin lesions by identifying and categorizing skin images
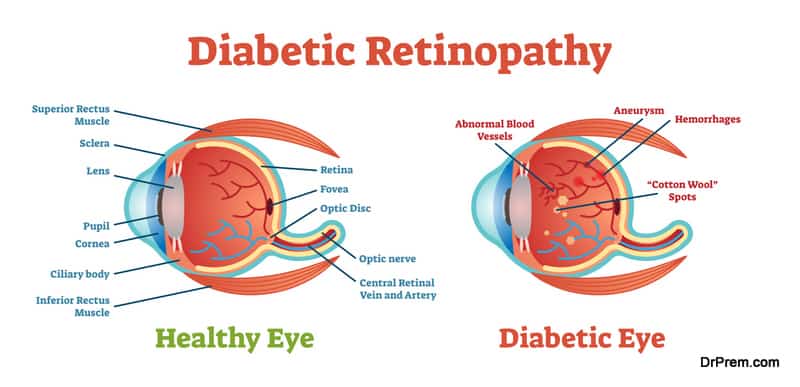
- Diabetic retinopathy by spotting indicators in eye images
Availability of abundant data related to these diseases has made AI-driven diagnostics more accurate and time-saving. In split second, AI can make the diagnosis. Above all, this data can be shared all over the world without incurring too much cost.
More advanced applications of artificial intelligence in diagnosis would involve a combination of multiple sources of data like CT scan, MRI, genomics, protemics, patient data and even handwritten files.
Advanced diagnosis in eye and colon diseases:
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults worldwide. Google researchers have come up with a deep learning algorithm that automatically detects the condition accurately. With a sensitivity score of 80-90%, the software’s accuracy is 98% in identifying the specificity of the disease categorizing as moderate or severe.
Another great AI application in eye-disease diagnosis has been achieved by doctors at Moorefield Eye Hospital in London. They taught an algorithm to recommend the right treatment approach for over 50 eye diseases with 94% accuracy. While comparing the results with that of eye-specialists, they were surprised to find that doctors missed a referral but not the AI.
Diagnosing colon polyps:
One of the vital applications of AI for doctors is the effective diagnosis of colon polyps. In a randomized trial, doctors in China found that AI significantly increased colon polyps detection rate by 29% (compared to 20% without AI). Doctors with AI support can spot very tiny polyps less than 5mm in size which are likely to be missed by experienced gastroenterologists.
Faster drug development:
Developing drugs is an arduous, time-consuming and expensive process. Applications of artificial intelligence in medicine have made drug development a much efficient process, saving years of hard work and millions of investment. AI has been successful in providing due support in all the prime 4 stages of drug development.
This is how it works:
Stage 1: Identifying target molecules:
This requires an understanding of the disease pathways and resistance mechanisms. Next comes identification of targets normally proteins to treat the disease. With the availability of screening and deep-sequencing techniques, huge data is available. Studying this data helps in finding viable pathways for attacking the target.
Traditional techniques make it extremely strenuous and time-consuming to integrate all these data collected from different sources. AI machine learning quickly analyses the available data and automatically identifies suitable target proteins.
Step 2: Discovering drug candidates
The next task is finding out the right compound to react with the target molecule in the most desired way without creating any toxic effects. This needs screening of thousands and millions of compounds having the potential to interact with the target protein. This involves a lot of trial and error before narrowing down to selected potential leads. Machine learning does this filtering very fast by predicting the potentiality of the molecule and the results are near accurate.
Step 3: Speeds up clinical trials:
Selecting suitable candidates is one of the crucial factors in achieving breakthroughs in clinical trials. AI helps in detecting suitable candidates based on specific patterns. It can also send warnings in case the trial is not producing desired results, saving time and money for developing that drug.
Step 4: Find biomarkers for diagnosis:
Biomarkers (molecules found in body fluids, mainly blood) provide an absolute indication of the presence and absence of disease. Identifying these make diagnosis and treatment cheap and secure. It also helps doctors create the right treatment plan.
Finding biomarkers for a specific disease is time-consuming and costly. AI can automate the manual process by sorting molecules as good and bad. Clinicians, therefore, get the best analysis of prospects.
AI alone creates a vaccine successfully
SAM (Smart Algorithm for Medical Discovery has successfully created the turbo-charged version of the flu vaccine. It contains a special compound to stimulate the human immune system making it more effective than the previous version.
The scientists trained SAM with a massive data of compounds some of which are immune-stimulating while some are not. A computer program containing trillions of untested compounds was generated. Based on the chemical compound training, SAM was able to detect compounds that could have a better effect on the human immune system.
Based on SAM’s selection, the researchers created prototype vaccines and tested on human blood cells. The results were extremely satisfying as SAM could efficiently pick the effective compounds. The drug is yet to pass the clinical trials but results so far are highly promising. If things go well, SAM-created enhanced flu-vaccine would be available for public in the next few years.
Enhanced robotic surgery:
AI-assisted robotic surgery has revolutionized global healthcare. AI can analyze data from pre-operative records and provide real-time guidance to surgeons towards better outcomes. Citing information from other surgical cases, it can also guide surgeons with newer techniques.
In a study, AI-assisted robotic surgery resulted in a five-fold reduction in post-operative complications and also 21% reduction in hospital stay. According to the analysis, AI-assisted surgery, if properly applied, can cause fewer complications and errors and generate nearly $40 billion in annual savings.
Aiding in personalized targeted treatment:
Personalization in treatments is gaining importance in global healthcare. All patients do not respond similarly to drugs and schedules even if they suffer from the same disease and show similar symptoms. Personalized drug administration can help in faster cure and increase the life span of patients.
It is tough to identify the factors affecting the treatment choice, but machine learning algorithm can quickly identify similar patient patterns and compare the treatments and outcomes. The resulting predictions make the job of physicians easier to frame the right treatment plan.
The advent of genomics has created a revolution in personalized medicine. The same thing can be more effectively administered in cancer immunotherapy with AI support. With high efficiency, AI can analyze complex data sets allowing more targeted therapies based on the patient’s unique genetic makeup.
Enhanced gene-editing:
CRISPR gene editing, especially with Cas 9 tool, is a big leap towards enhancing the gene-editing technique. It demands the highest level of accuracy as it relies on short guide RNAs to target the specific location of the gene and edit it. Since sgRNAs can fit multiple DNA locations, it is important to find the right sgRNA. Else the chance of undesirable side effects is much higher.
The possibility of undesirable side effects is a major stumbling block in CRISPR application. Here machine learning has been proven to give accurate results in predicting the degree of both guide and target interactions of a given sgRNA.
Personalized nutrition:
Eating according to individual’s nutritional requirement and physical condition is the key to good health. Just making healthy food choices won’t do. You need to pick food according to your body. AI in personalized nutrition is a much-debated topic but shows enough promise.
For example, AI can help in preventing glucose spikes after meals by suggesting individualized eating plans. Although the studies are in the nascent stage, emerging data from ongoing work are gaining traction.
Helping in treating anxiety and depression:
AI-driven chatbots and Avatars can help people come out of depression. The researchers at the USC used avatar Ellie to test whether people suffering from depression will share their mental condition elaborately to a bot than to a human. It was found people are ready to share the deepest secrets with a bot. It is like a confession with a cathartic effect.
Some consider it as a breakthrough, while some are skeptical. But given the serious mismatch in the requirements to support people’s mental health and that available, AI-driven avatars and chatbots seem to be more promising.
For the first time, AI is helping in getting real-time objective metrics to understand the mental state by decoding typing pattern in smartphones, tone of speech, communication style and physical activity. More the data accumulation, better it will be for AI to provide insights for depression and anxiety treatment.
Freeing up doctor’s time:
The human touch in healthcare is fading fast. The doctor-patient interaction time has been reduced to a mere few minutes. The opportunity is dim to develop any rapport or connection between them. One of the most useful applications of AI for doctors lies in performance enhancement by ending redundant tasks.
AI, in true sense, can make time grow, allowing doctors to give more time to patients. It can help in redundant tasks like note-taking, writing tasks and other activities. A radiologist on an average reads 50-100 images every day. Error rates are high and a third of radiologists are likely to face malpractice suits at some phase of their career. With deep learning, radiologists can scale their performance of reading 10 or 100 times more films with minimum chances of error.
Evolution of medical practice with AI-assisted treatment management:
What about the radical changes that Applications of AI in medical practice can bring? AI can extract important patient information from electronic footprints. This not only saves time and enhance efficiency, but also plays a significant role in treatment management. Validated AI applications will be given more responsibility in treatment management.
By scanning innumerable data related to blood analysis and other diagnostic tests, AI can create a summary of the consultation on voice record and leave it to the physician to approve or amend. This will lessen the physician’s burden and also reduce patient waiting times. For a patient suffering from type 2 diabetes AI can give recommendations for commencing statin group of medicines.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is using AI tech IBM Watson not only in diagnosis, but also in creating effective treatment management plans for cancer patients. To accomplish this, it is synthesizing millions of records, patient-data, clinical trial reports and medical journals. The partnership between IBM and CVA Health is purposed for using AI application in chronic disease management.
Specialist diagnostic service in primary care:
AI applications have the potential to introduce specialist diagnostic service in primary care. The image of a skin lesion captured by the primary care GP can be sent to an AI-supported dermatology specialist for instant analysis. Low-risk patients will receive quick reassurance, while high-risk patients will face low referral waiting times as the clinic would be seeing selective patients, not all.
Future applications:
According to Health IT Analytics, the following list provides the future potential of AI in global healthcare:
- Integrating mind and machine through Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) helping in augmenting motor functions in some patients.
- Evolution of new tools in radiology.
- Improved care to the underserved.
- More effective use of EHRs making a predictive analysis.
- Reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance deriving insights from HER data analysis
- Improved accuracy in the analysis of pathology images
- Leveraging data from personal health wearables, smartphones and other digital devices.
Key healthcare management benefits with AI
Keeping healthy
AI helps people to stay healthy and active, thus reducing thenumber of doctors’ visits. This has been referred to as one of the important benefits of AI in healthcare management. The advancing technology and multiple apps are currently functional to give up to date information about your health, can encourage healthier behavior in you, can insist ona daily physical exercise routine and diet plan. Besides, AI has also been very helpful in programming patient’s health as well as disease condition and the same is presented to a medical professional to obtain better feedback, accurate guidance, and support system to stay healthy and active.
Early detection
Applications are presently being developed that can help patients to detect critical diseases, such as cancer, at a very early stage. According to the American Cancer Society, artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine can decode mammograms with 40 times faster efficiency and with 99% accuracy that can reduce the requirement of unnecessary biopsies. This way the prevalence of false positive results can be minimized to the considerable extent.
Moreover, with the combination of consumer wearables and AI, it has now been possible to detect early-stage heart disease and arthritis, enabling medical professionals and patients to continuously monitor health status, implement necessary precautions, and detect potentially life-threatening flare up much before time to save a life.
Disease Management
Artificial intelligence in hospital and medicine has been helpful to clinicians as it can present the clinicians with more comprehensive data – mentioning patient’s medical history, family history, stage of the disease, medication prescribed, allergies if detected during the course and/or adverse events noted in the course of treatment, etc.
Recently, Artificial Intelligence has been developed not only to assist surgeons in operation theaters, but also execute operations on their own with the help of highly complexed surgical robots.
Independence
In today’s digital world, people cannot take out time for managing their own health! AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we are living! It can be helpful for old people to be independent for longer period of time, can reduce the need for frequent hospitalization, can help them to have their medical visits at the comfort of their home, can get necessary care and nursing even at home – thus reducing the overall hassle of medical and nursing during their old age.
Faster discovery
According to the recent survey by the World Health Organization, it takes almost about 15 years for an investigational drug to pass through all the stages of its development till routine implementation in medical practice. Accordingly, only 1% of the total drugs that have been formulated can pass through regulatory compliances and only 1/4th of them can be implemented in clinical practice. In this regard, the application of AI in drug discovery and formulation has been increasing to streamline the process of discovery and speed up the stages of clinical studies and regulatory compliance.
Considering the huge potential of AI application in healthcare, the medical world is excited and is looking forward to the routine application of AI in medicine.
Is everything good with AI applications in medicine?
Even though the potential is immense, there are few areas of concern. Are global healthcare systems prepared to embrace AI-assisted medicine support? The prime liability is hacking and breach of privacy and the lack of providing explanations in most algorithms. Any misleading data fed can create misleading results.
The regulation of AI algorithms poses a difficult task. The USA FDA has approved only a few such algorithms, but there is no universal regulation guideline to follow. Another important obstacle is that the people creating algorithms are not physicians or specialists. They may not always be in a position to have a clear understanding of all perspectives. Clinicians also need to have a better understanding of what the algorithm is specified to do and what not to do.
In clinical trials, FDA maintains strict acceptance criteria and demands extreme transparency of all the scientific methods adopted. Algorithms often rely on very intricate and complex mathematics from the input data to the final result. Proprietors of such algorithms may not be willing to expose their proprietary methods. Can FDA approve such AI dependant trials? AI algorithms may also fail to win the trust of patients and clinicians.
Healthcare is still far away to witness AI operating independently in clinics. Overcoming challenges is worth trying to universally increase the efficiency and accuracy of medical treatment practices.