Coenzyme Q10 was discovered in 1957 by Dr. Frederick Crane. The compound is made from our body and remains stored in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells. Production of coenzyme Q10 decreases with aging. Therefore, elderly people are likely to suffer from its deficiency which is manifested through Vitamin B6 deficiency. This substance occurs in the plants and animal tissue. In animals, including human beings, it is found in kidney, liver, heart and pancreas.
Food types which have coenzyme Q10
Foods rich in CoQ10 are beef, chicken, pork, fish, vegetables, oils, nuts, fruits and dairy products. Liver, kidney and heart are the areas where maximum amount of this substance is found.
Why coenzyme Q10
It is very effective in reducing cholesterol and triglycerides levels, at the same time it also helps in improving the levels of lipoproteins in our body.
Helps boost immune function, especially in those with immune system deficiencies. It is also an antioxidant which helps protect cells against damage caused by free radicals.
Regular intake of Coenzyme Q10 benefits patients suffering from migraine headaches.
CoQ10 is also being investigated as a treatment for cancer, and as relief from cancer treatment.
Studies have shown that coenzyme Q10 can benefit the patients suffering from hypertension.
It has been shown that low levels of coenzyme Q10 is directly linked to heart failure. One of the key reasons for heart failure is oxidation of lipoprotein (LDL) which leads to pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and that is what leads to a heart attack. It has been proved that if sufficient quantity of coenzyme Q10 is present in human LDL, it helps protect against the process of LDL oxidation, thus reducing the atherogenic potency of LDL.
Coenzyme Q10 helps prevent periodontal disease. It has been shown that diseased gum tissue is deficient in coenzyme Q10 as compared to healthy gum tissue. Clinical trials in human beings have suggested that oral intake of coenzyme Q10 leads to higher immunity to gum disease and improves oral health and also reversing of diseased gums.
A study was done on rats where they were given small amounts of coenzyme Q10 and polyunsaturated fats lead to increase in their life span.
Helps slow the progression of neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease, beneficial in chronic fatigue syndrome, protects blood cells from radiation and is great for your skin.
There are no side effects of Intake of upto 1600 mg over a long period of time. Individuals who have poor indigestion or issues with their intestinal tract should apply discretion.
9 Best food sources of coenzyme Q10:
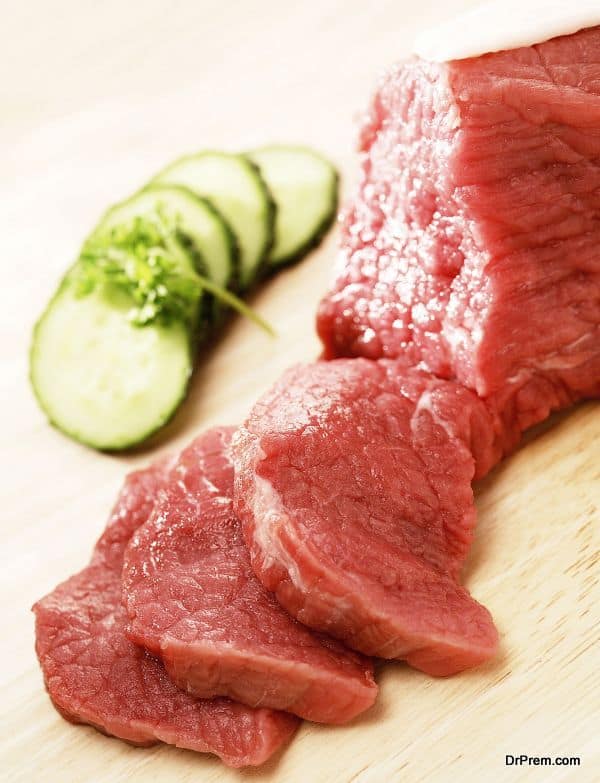
Beef
Beef is considered the richest food source of coenzyme Q10, which can be found in the heart, liver and muscles in varying quantities. Heart contains upto113 mg per kg, liver contains up to 50 mg per kg and muscles contain up to 40 mg per kg.
However, this may not be suitable for everyone, people avoid beef for various reasons, primarily for religious beliefs and food habits. If consumed regularly it can take care of our daily intake of coenzyme Q10. It is widely available in most regions.
Standard servings of beef are of 3 ounce.
It needs to be highlighted that coenzyme Q10 is naturally found in all organisms specially liver, kidney and heart of animals and also in the tissue in plants.
As for side effects, beef if consumed is large quantities can lead to increased cholesterol and high blood pressure. Therefore, it should be consumed in small to moderate quantities.
Vegetables
Although vegetables are considered a moderate source of coenzyme Q10, they are still a good source specially if they are consumed after boiling instead of frying.
Good sources are parsley 26mg/kg, broccoli 9mg/kg, cauliflower 7mg/kg, spinach 10 mg/kg and Chinese cabbage 5mg/kg.
Standard servings of vegetables depends from region to region and can vary from 2 ounce servings to 15 ounce in a single serving.
Vegetables are widely available and unless advised by a medical practitioner, one can have them on a regular basis by practically anyone. They are very much part of all types of diets all over the world.
It needs to be pointed out that they do provide enough CoQ10 to meet the minimum requirements, however, if you wish to increase your intake, you might want to add items that have high CoQ10 content.
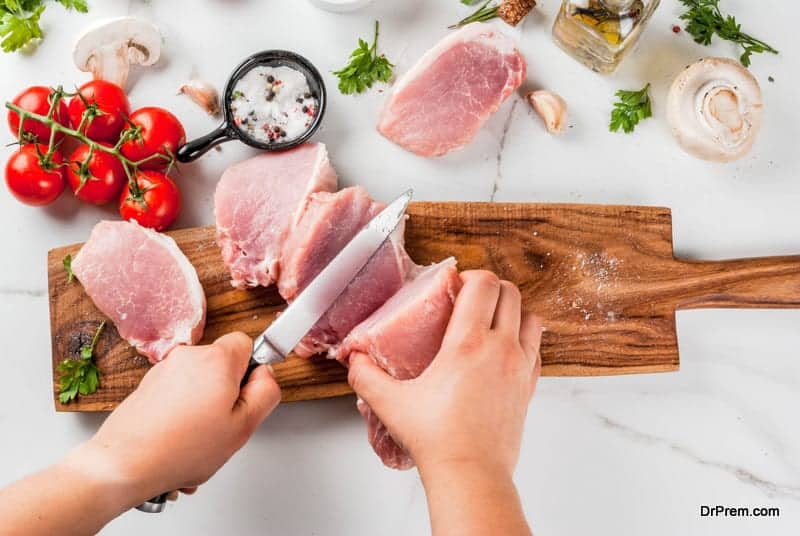
Pork
Pork is a good source of coenzyme Q10 and is widely available, as usual some people are averse to eating pork due to cultural and religious beliefs and some avoid it due to food habits. It can contain up to 128 mg/kg and a 3 ounce serving can provide sufficient amount of CoQ10.
Standard servings of pork depends from region to region and can vary from 2 ounce servings to 10 ounce in a single serving.
It can be consumed by people of all ages, gender, race, etc., unless otherwise advised by a medical practitioner.
Eating too much pork can cause high blood pressure, cholesterol, cancer, heart problems, and obesity.
Chicken
Chicken is another food item which contains upto 133 mg per kg of Ccoenzyme Q10. It is most widely available and for non-vegetarians, it is considered staple all across the world. Dishes made out of chicken are widely cooked and consumed in all parts of the world.
Standard servings of chicken depends from region to region and can vary from 2 ounce servings to 12 ounce in a single serving.
People of all ages all over the world can have it unless otherwise advised by a medical practitioner. There are no side effects unless consumed in large quantities which might lead to indigestion.
Too much chicken can lead to kidney stones apart from high cholesterol if cooked with large amount of salt and oil.
Fish
Fish are an excellent source of coenzyme Q10. Fish known for its high coenzyme Q10 content are sardines 64 mg/kg, mackerel red flesh 67 mg/kg, white flesh 16 mg/kg, salmon 8mg /kg and tuna 5mg/kg.
In some parts of the world, they form part of the staple diet and in other parts they are seasonal and are not available throughout the year.
They can be consumed by people of all ages unless advised against by a medical practitioner.
Standard servings of fish depends from region to region and can vary from 2-4 ounce ounce per serving.
Fish and fish oil should be avoided by pregnant women and children as omega 3, which is found in large quantities in various types of fish, increases the breaking down of blood clots and decrease blood platelets from clumping together and babies are most susceptible to this.
Oils
Oils are a good source of coenzyme Q10 as well. Soyabean oil (280mg/kg), olive oil (160 mg/kg), grape seed oil (73mg/kg), and sunflower oil (15 mg/kg) are all rich in coenzyme Q10.
These oils are generally used for cooking but can also be used as an ingredient in various dishes. One to three teaspoons is what would generally be used while preparing a dish.
Different cultures are used to using specific oils when preparing their meals. 1-2 spoonfuls are used while cooking, in some dishes, a sprinkling is used for garnishing or for aroma.
Oils are not consumed directly, although they can be consumed by people of all ages in small to medium quantities. There are no known cultural or religious blocks to usage of oil.
If used properly, they can be a good source of CoQ10.
If consumed in large quantities, it can lead to high cholesterol, obesity and heart disease.
Nuts
Nuts are another good source for coenzyme Q10. Examples of nuts are peanuts (27mg/kg), walnuts 19 mg/kg, sesame seeds 23mg/kg, pistachio nuts 20 mg/kg, hazelnuts 17 mg/kg and almond 14 mg/kg.
These are considered as a good snack and can be taken separately or be used in dishes.
The serving size depends on various factors and may vary greatly.
Nuts have always been considered a side dish or a snack in most cultures. They can be consumed by people of all ages up to a limit unless otherwise advised.
Nuts if overeaten can lead to weight gain.
Fruits
Fruits are a poor source of coenzyme Q10 with the exception of avocado.
Some examples of fruits with their corresponding levels of CoQ10 available are grape 7mg/kg, avocado 10mg/kg, blackcurrant 3mg/kg, strawberry 1mg/kg, orange 2mg/kg, grapefruit 1mg/kg and apple 1mg/kg.
Due to their wide availability and they can easily be found and consumed on a regular basis. However, fruits on their own cannot provide sufficient dietary CoQ10.
There are no side effects and they can be consumed by everybody irrespective of age, gender and geography. The only limitation is most fruits are seasonal.
The only side effects of fruits is if you consume the peels and skins, as that contain insoluble fiber, it leads to gas.
Eggs and dairy products
Eggs and dairy products have moderate to small quantities of coenzyme Q10.
Dairy products are the most widely available and unless you have an allergy to any particular ingredient or are a complete vegetarian, it can be a goo source of CoQ10. However, it needs to be kept in mind that dairy products are poor source of CoQ10.
As compared to the meat sources, they do not provide adequate CoQ10.
On the other hand, large intake of CoQ10 can lead to issues with people suffering from indigestion.
It also needs to be kept in mind that if there are any allergies, then one needs to regulate the intake of dairy products, for example if one has lactose intolerance, then we need to reduce intake or increase intake of magnesium so that we can increase absorption of calcium found in milk.