Eco-friendly energy is being derived from every viable source. This includes humans too. There are devices which will be powered by the energy powered by your own body. No need for batteries and any other external energy source. You may have to do some work for it, however. You might have to pedal or walk to power wearables and so on. Harvesting energy from humans is what scientists are working on now. Body heat, blood flow, and even sweat may become fuel for your daily activities. Take a look:
Harvesting energy from humans is the latest trend in green energy
 When you breathe, your lungs make a motion like a bellow. This generates .83 watts energy and your body heat produces 4.8 watts, while moving your arms creates approximately 60 watts of energy. Human power energy can be used for things like hearing aids which needs only one thousandth of one watt, pacemaker requires 50 millionths of one watt and your smart phone needs only one watt. So, it means that harvesting energy from humans can effectively power devices which require very little energy.
When you breathe, your lungs make a motion like a bellow. This generates .83 watts energy and your body heat produces 4.8 watts, while moving your arms creates approximately 60 watts of energy. Human power energy can be used for things like hearing aids which needs only one thousandth of one watt, pacemaker requires 50 millionths of one watt and your smart phone needs only one watt. So, it means that harvesting energy from humans can effectively power devices which require very little energy.
Harvesting energy from blood flow
 Swiss scientists and biomedical engineers are experimenting how to harness human kinetic energy. They are studying if microturbines implanted in the arteries of human beings can be used to generate power. The interesting experiment shows that microturbines in the arteries can work like hydroelectric power plants. These turbines would use blood flow instead of water flow to create electricity.
Swiss scientists and biomedical engineers are experimenting how to harness human kinetic energy. They are studying if microturbines implanted in the arteries of human beings can be used to generate power. The interesting experiment shows that microturbines in the arteries can work like hydroelectric power plants. These turbines would use blood flow instead of water flow to create electricity.
Till now, the researchers have found that these microturbines generate 800 microwatts of electricity. This harvesting energy from humans is more than enough for pacemakers. In some cases, this innovative green energy has powered blood pressure devices, neurostimulators, and drug delivering pumps.
Piezoelectric energy harvesting devices
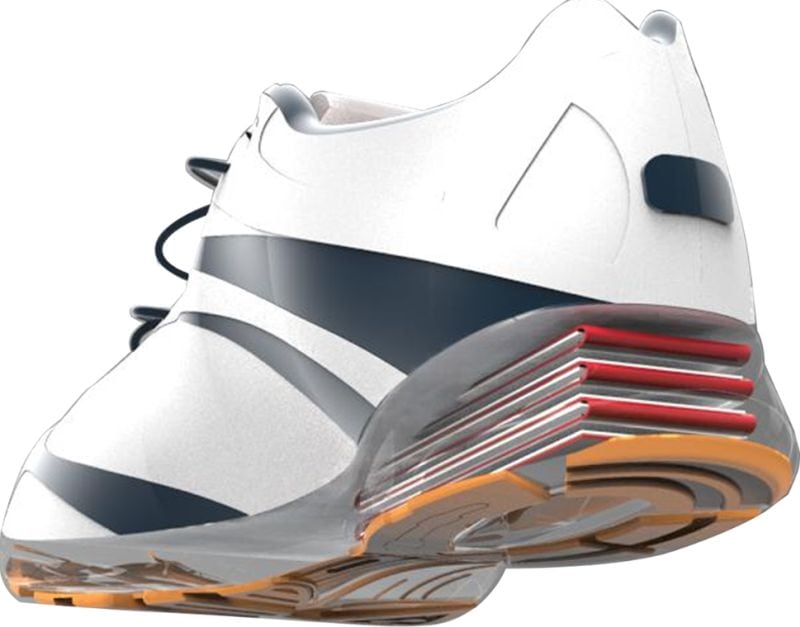

Image Source : internapcdn.net
A method to harvest energy is to convert vibrations, mechanical stress pressure,etc into electricity. This method is usually used in microphones and loudspeakers. The material which is most commonly used is lead zirconate titanate. This material’s lead content might be too toxic for use within the human body, which could be a potential drawback.
But the researchers say that it would require 700 degrees Celsius for lead to melt. The human body never heats to that extent. The miniature lead devices can be implanted within the body, specifically in the lungs, heart, and diaphragm. These devices do not disrupt the tissue functions after implantation.
As of now, these devices which harness human power energy have been tested in sheep, pigs, and cows. Due to the organ functions, the devices distort and create negative and positive energy, current, and voltage. This energy can be collected to recharge batteries of pacemakers, eliminating the need to change them every few years.
Other piezoelectricity harvesting devices enabling harvesting energy from humansare being developed which can be worn on the joints like the elbow, knee, or in shoes. Whenever a person moves his arms or bends them, electricity will be generated.
Body heat
An innovative method to harvest potential energy in the human body is to use thermoelectric materials to convert body heat into electricity. The human heart beats 40 million times in a single year. The energy generated by the beating of the heart gets dissipated as body heat. Scientists say this heat can be used to generate power.
One of the devices being tested now is made from glass and fabric. This machine can fit into the curves of a person’s wrist and capture body heat. The only difficulty in harvesting body heat energy is that there is not much difference in the heat produced by the body. The difference can be created by keeping the devices in an environment which is cooler than the body.
Harvesting energy from humans in this manner will potentially be used to power wristwatches, health monitors, deep brain stimulation machines, and cochlear implants.
Footsteps
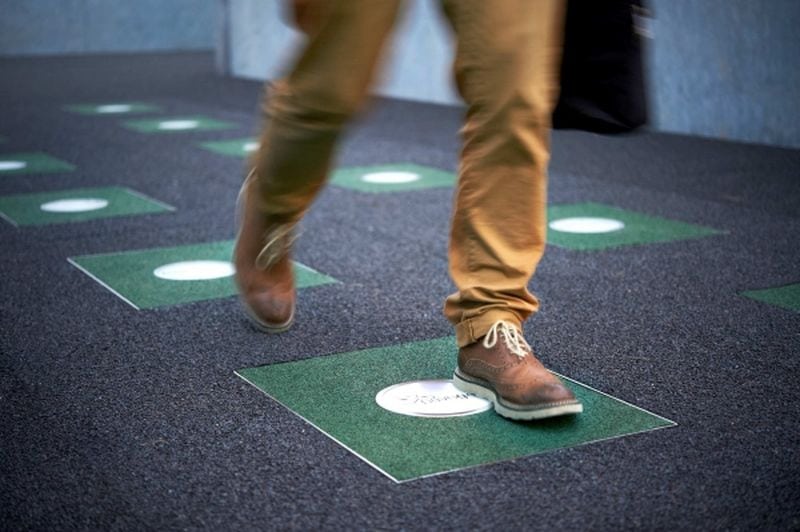 Image Source : thecivilengineer.org
Image Source : thecivilengineer.org
Your footsteps can also be used to generate energy. A company called Pavegen has been researching on how to harness human kinetic energy. The startup has designed tiles which can produce electricity when anyone steps on them. 1-7 watts of energy can be generated which is enough to power an LED for about 30 seconds. The technology will also be useful to track the walking patterns of humans. Pavegen aims to price the flooring equal to regular tile, which might result in many more people choosing these unique tiles.
Exercise
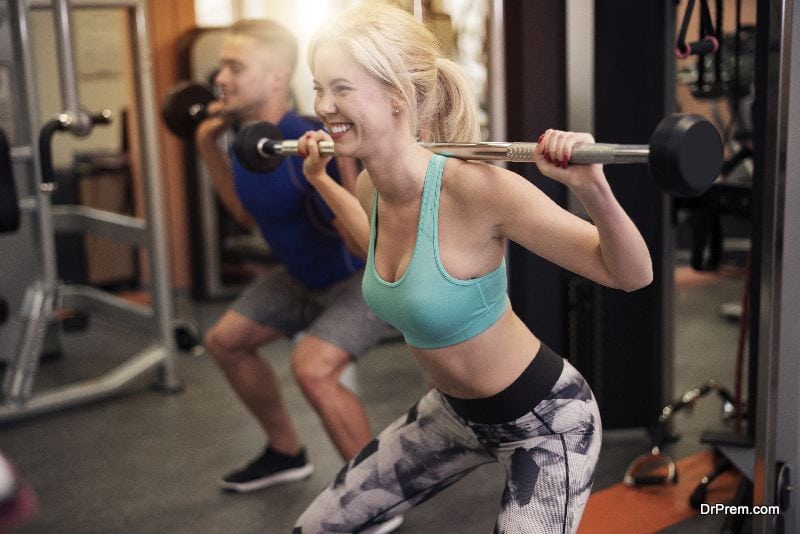 At your gyms, as in other gyms all over the world, there are elliptical trainers, bicycles, steppers, and many more machines. These machines could generate electricity too. This method of harvesting energy from humans is actually being used in many gyms in US. The machines are wired up with DC generators and are connected to one central unit which has an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity to AC current and sends it to the building’s grid.
At your gyms, as in other gyms all over the world, there are elliptical trainers, bicycles, steppers, and many more machines. These machines could generate electricity too. This method of harvesting energy from humans is actually being used in many gyms in US. The machines are wired up with DC generators and are connected to one central unit which has an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity to AC current and sends it to the building’s grid.
Some exercise machines have ‘hand cranks’ as well as pedals which can turn a flywheel. This flywheel is connected to a generator.
These electricity producing exercise machines do not really produce a large amount of electricity. An average cyclist would produce 50-150 watts and hour, whereas a top cyclist can generate 400 watts. This is very nominal, but as the manufacturers of these machines say, every bit counts.
Triboelectricity
 Have you ever experienced suddenly getting a small shock from some device or fabric, even if they are not connected to anything? This happens due to triboelectricity, a phenomenon in which a surface ‘steals’ electrons from another surface (even your hand).
Have you ever experienced suddenly getting a small shock from some device or fabric, even if they are not connected to anything? This happens due to triboelectricity, a phenomenon in which a surface ‘steals’ electrons from another surface (even your hand).
Almost all materials, both natural and synthetic,are capable of doing this. This electricity can be produced by fitting shoes with triboelectric generators. When you walk, the generator will produce electricity. Imagine if you are going hiking or trekking, you could probably charge your devices just by all the walking.
Harvesting energy from humans and using it for their own needs is a worthwhile proposition. It would reduce the use for batteries for pacemakers, cochlear implants, body monitors, etc. These devices would also have the property to dissolve within the body after their use is over.

