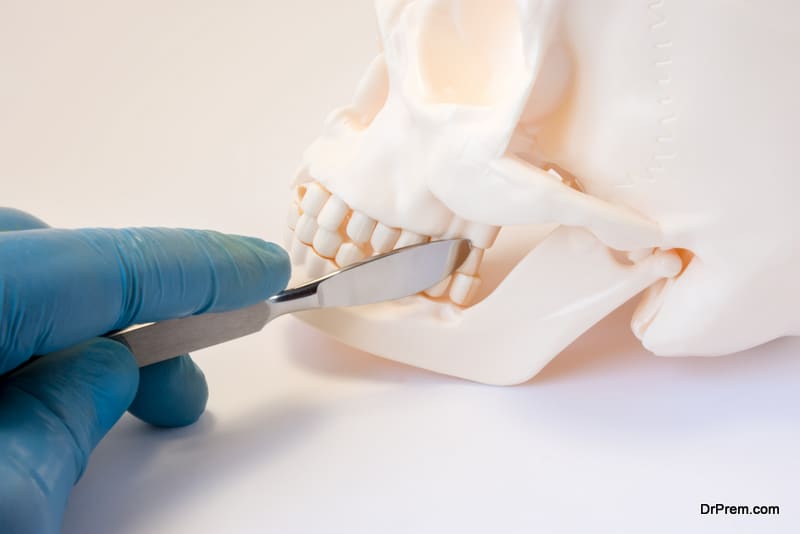
Definition:
Maxillofacial surgery is a specialized surgery of the face and jaws performed to correct deformities, treat diseases and repair injuries. This surgery is performed by a specially qualified and trained surgeon, known as an Oral & Maxillofacial surgeon.
Why it is needed:
The conditions in which maxillofacial surgery is advised include:
- Facial injuries due to severe accidents
- Birth deformities
- Severe orthodontic deformities
- Gum disease
- Cancer patients with facial tumour
Facts and Figures:
- Maxillofacial surgery is one of the nine specialties of dentistry.
- Hugo Obwegeser was honoured as a pioneer in orthognathic (facial skeletal) surgery; he has been instrumental in introducing the orthognathic surgical technique to US surgeons in the 1960s.
- The famous surgeon Luc Chikhani reconstructed Trevor Rees-Jones’s face, who had severe facial injuries due to the car crash that killed Diana, Princess of Wales.
- Cases of maxillofacial injuries are common in emergency medicine.
- More than 3 million facial injuries occur in the United States each year. Most of them are victims of motor vehicle accidents.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Maxillofacial surgery corrects the deformities and treats the injuries.
- Improves appearance of a face that has been disfigured by injuries or tumour and helps patients regain self-esteem and confidence.
- Relief from pain and discomfort caused by gum disease
Disadvantages:
- Permanent facial deformity due to improper treatment
- Damage to the facial nerves resulting in loss of sensation, facial movement, smell and/ or taste
- There could be rejection of bone graft and non union of fractured bone
- Scars on the face
Risks and Complications:
- Reaction to anaesthesia or medication.
- Bleeding
- Infection of surgical wound.
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Incomplete correction or treatment.
- Muscular damage
- Chronic sinusitis
Pre-operative and Post-operative care:
Pre-operative preparation:
- Complete physical examination
- Blood and urinalysis
- Consultation with surgeon or doctor a week prior to procedure; doctor will prescribe necessary medication and advice on medicines that have to be discontinued.
- Inform the surgeon about smoking and alcohol consumption patterns.
- Arrangements for leave from work, help at home, help with driving and during post surgery recovery period.
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before surgery.
- Medical tourists are advised to select a comfortable hotel room equipped with handicapped facilities, for recovery after hospital discharge.
Post-operative care:
- Patients need to take medication regularly as instructed by the surgeon to control pain and ensure proper healing.
Do’s, Dont’s and Precautions:
- Do not rinse or spit for 24 hours after surgery.
- Keep fingers and tongue away from socket or surgical area.
- Do use ice packs on surgical area (side of face) for first 24 hours; apply ice 20 minutes on, 10 minutes off.
- Do drink plenty of fluids (do not use a straw).
- Chewing gum at intervals will help to relax the stiffness of muscles.
- Use of warm, moist heat to the outside of face over muscles will help to reduce stiffness in the jaw.
- Do rinse with warm salt water following each meal, after the first post operative day.
- Avoid seeds, nuts, rice, popcorn, etc; instead eat soft, easily chewable food.
- Apply pressure to surgical area using small rolled gauze for 90 minutes to control bleeding.
- Don’t smoke until the wound heals properly.