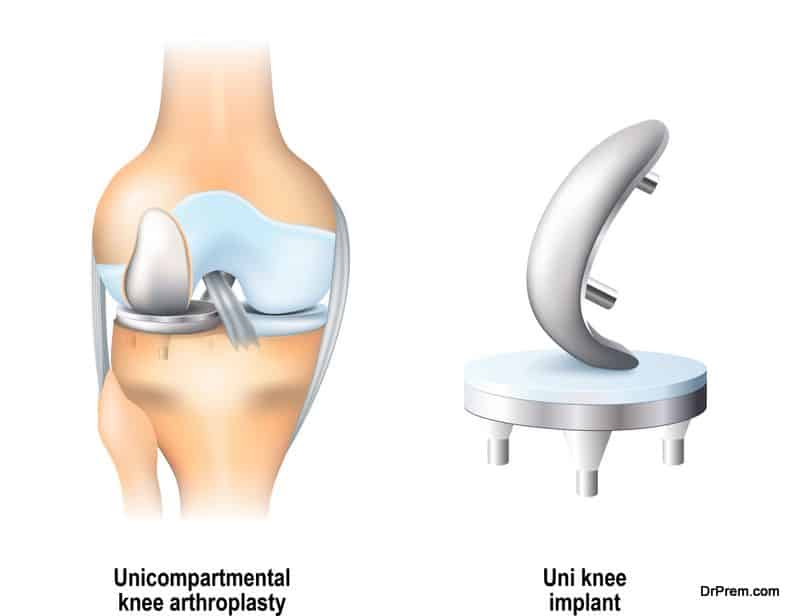
Definition:
Total knee replacement (total knee arthroplasty) is performed to treat and to restore the function of painful, disabled knee joints. The affected knee joints are replaced by artificial knee joints which are a combination of metal and plastic and are available in various designs. The metal meets the end of the bones and a plastic spacer acts as buffer between them.
Details of procedure:
Total knee replacement is recommended, when the severe knee pain:
- Causes disturbance in sleep at night
- Has not improved with other treatment
- Limits the patient’s day to day activities
Or the pain and limited function of the knee could be due to:
- Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Accidental injuries to knee joints
Facts and Figures:
- The knee joint is one of the strongest, largest and most complex joints of the body. Normally a man of 70kg weight will apply about 210kg of force on the knee while playing football, basket ball and running.
- The artificial knee replacement surgery for arthritis is considered as one of the most successful surgeries in modern era.
- There are about 270,000 knee replacements surgeries performed each year in the United States (AAOS). Approximately about 70% of these surgeries are performed on persons over the age of 65.
- The first artificial implants inspired by successful hip replacement surgery, were tried in the 1940s.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Total knee replacement surgery has a high success rate; approximately 95% of patients experience relief from the symptoms after surgery.
- Total knee replacement provides a patient with relief from joint pain and increased leg strength and mobility.
- Total knee replacement has a longer life span of about 10 to 15 years.
- The surgery improves quality of life by allowing patients to participate in the activities which were restricted prior to surgery.
Disadvantages:
- Unwanted stiffness of joint and loss of knee motion
- Patellar complications can occur
Risks and Complications:
- Loosening of the prosthesis from the bone.
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Anaesthetic reactions/breathing problems
- Excessive scarring
- Blood clot
- Medicinal or anaesthesia reaction
Pre-operative and Post-operative care:
Pre-operative preparations:
- Complete physical examination
- Blood and urinalysis
- ECG and X-ray of chest for patients above 50 years of age.
- Consultation with surgeon or doctor a week prior to surgery; doctor will prescribe the necessary medication and advice on medicines to be discontinued.
- Inform the surgeon about smoking and alcohol consumption patterns.
- Visit to physical therapist to know about the post surgery rehabilitation program and guidance on the use of crutches or a walker.
- Arrangements for leave from work, help at home, help with driving and during rehabilitation program.
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before surgery.
- Pack a supply of comfortable clothes.
- Medical tourists are advised to select a comfortable hotel room equipped with handicapped facilities, for recovery after discharge from hospital.
- Arrangements for blood donation, if required during surgery.
- Arrangements at home considering post surgery rehabilitation.
Post-operative care:
- After the surgery patient needs to wear a special compression stocking on legs to improve blood flow and proper healing.
- Patients are advised to start light activity from the first day after surgery and are supposed to use crutches or a walker post surgery.
- It is important for patients to do the exercises regularly as per the instructions of the physical therapist, to achieve optimal result from the surgery.
- Patients can begin physical therapy 48 hours after surgery.
- Normal recovery after surgery is seen within 7 to 10 days. Patients will be discharged from hospital only after the following criteria are met:
- Able to bend knee at a 90 degree angle.
- Get out of bed without any support.
- Able to extend knee straight out.
- Can walk using crutches or a walker.
- Keep doing regular prescribed home exercises to restore your knee.
Do’s, Don’ts and Precautions:
- Do strictly follow the prescribed diet regime.
- Do take prescribed medicines on time.
- Do exercises regularly as advised by physiotherapist.
- Early mobilization will help to strengthen the knee muscles.
- Don’t take a bath until the sutures or staples are removed.