At school, I took great pleasure in collecting colorful erasers, pencils and pencil boxes from my classmates’ bag. Not that I needed them badly but it was somewhat of a satisfactory feeling of possessing so many things. I wasn’t aware of the act of stealing.
An irresistible and recurrent urge to steal things that are not required or have little value is known as Kleptomania. Kleptomania in children is not much heard of. The childish habit of picking up other’s belongings often subsides on its own.
But this may not happen universally. The problem may be severe with adolescents and teens. If the practice continues, your child might have developed some compelling psychological reasons for stealing. He/she needs medical attention.
A child who steals at a tender or grown up age is likely to be bullied and abused by school mates. This does not augur well for his/her mental development. He/she will be lagging in all respects.
How to identify a Kleptomaniac child?
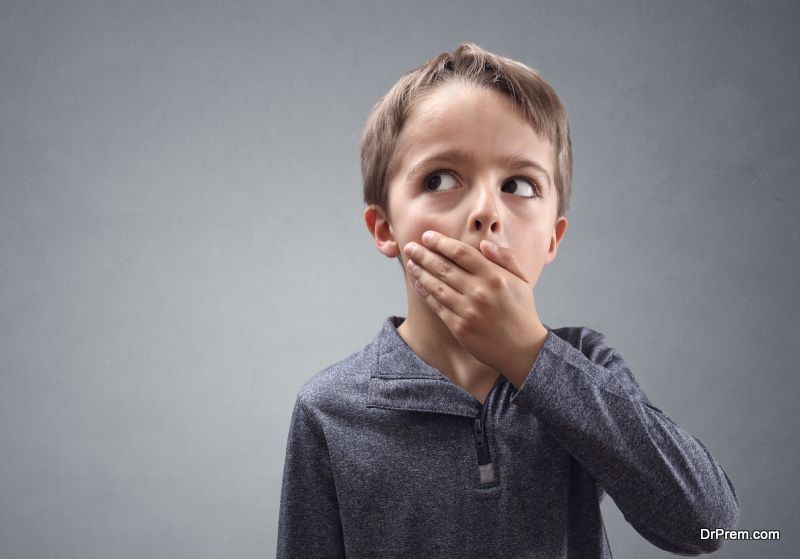 Accepting the child to be a Kleptomaniac is a trying time for the parents. But observing certain symptoms in your child may help in dealing with the situation better. The child who steals is under severe mental tension but experience pleasure and relief after committing the act. He/she feels glad to have stolen the object of his/her desire.
Accepting the child to be a Kleptomaniac is a trying time for the parents. But observing certain symptoms in your child may help in dealing with the situation better. The child who steals is under severe mental tension but experience pleasure and relief after committing the act. He/she feels glad to have stolen the object of his/her desire.
It is a lone act and kids are very cautious about maintaining its secrecy. Children with Kleptomania do suffer from shame, guilt and fear always dreading of getting caught. Another important symptom of Kleptomania is that most of the objects stolen by kids are not used but just hoarded.
Common psychological reasons for stealing in a child:
 Kleptomania in children is not always a big concern. The general trend of stealing as suggested by child development experts can be summarized as follows:
Kleptomania in children is not always a big concern. The general trend of stealing as suggested by child development experts can be summarized as follows:
- Many children like to take home certain things not belonging to them.
- 2-4 yr- old kids will take things as they are yet to have a clear idea between yours and mine and general sharing. This cannot be labeled as stealing.
- Most of the 5-8 year-old kids are aware of the ownership. When they take something which is not theirs, they will try to hide it and deny the act when confronted. They often lack self-control. This is also normal. Parents should be concerned of this behavior but need not worry too much considering it as a never-to-die habit.
- With kids aged 8 years or more, this can be a real concern. They do not refrain from the stealing habit in spite of being corrected a number of times.
Other significant psychological reasons for stealing can be:
- Kids may be anxious or angry and attention seekers. This stealing act may be the result of stress at home, school or with friends. This behavior signals as a cry for help if they are enduring serious physical and emotional abuse.
- Not being able to afford to buy certain items is another compelling reason for the child to steal. They may steal to possess some popular branded items or may do so to support their drug habit.
Causes of Kleptomania in children:
The exact causes of Kleptomania in children are yet to be understood fully. It may be a result of environmental, psychological and biological factors.
1. Brain activity pattern in a Kleptomaniac:
A decrease in the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain is often associated with risk-taking behaviors. Mood and emotions of a person are regulated by serotonin. Moreover, there may be also a surge in the dopamine levels, a neurotransmitter activating the pleasure center of the brain. This triggers the stealing act which gives pleasure to the child.
2. The stolen object may symbolize something else:
In psychological treatments with Kleptomaniac, it was found that the stolen object is not the ultimate want of the child. It may symbolize something else. Kleptomania in children could arise from certain unfulfilled wishes which they do not wish to disclose or speak out. The object stolen fulfills this unspoken desire in the most complicated manner.
3. An act of coping with deprivation or loss:
 Kleptomania in children is not only related to impulsive actions. Children experiencing a real or imaginary loss or deprivation may take to acts of stealing. The objects stolen help them to cope up with their pain of loss. It carries immense significance which is related to the trauma faced by the child.
Kleptomania in children is not only related to impulsive actions. Children experiencing a real or imaginary loss or deprivation may take to acts of stealing. The objects stolen help them to cope up with their pain of loss. It carries immense significance which is related to the trauma faced by the child.
How to stop your child from being Kleptomaniac?
Kleptomania in children can be treated. These children are not criminals. They are suffering from a disorder. Too much of scolding and ridiculing will simply worsen the problem. If the stealing habit of children couldn’t be managed by parents, it is important to consult a psychologist or therapist.
Tips you can follow to stop your child from stealing:
1. Do not overlook the problem:
 Children like to possess other’s things that they do not have. It is more of a childish act than stealing. Everyone knows that. But parents must be watchful if their kids pick up this habit and try to nip in the bud.
Children like to possess other’s things that they do not have. It is more of a childish act than stealing. Everyone knows that. But parents must be watchful if their kids pick up this habit and try to nip in the bud.
2. Do not punish the child:
Awarding punishment worsen things. Kids become obstinate. Parents should counsel their children explaining them it is not a good act. They should guide kids to return the stolen objects and seek an apology. The child would not feel like repeating the act.
3. Praise the child for making up the damage:
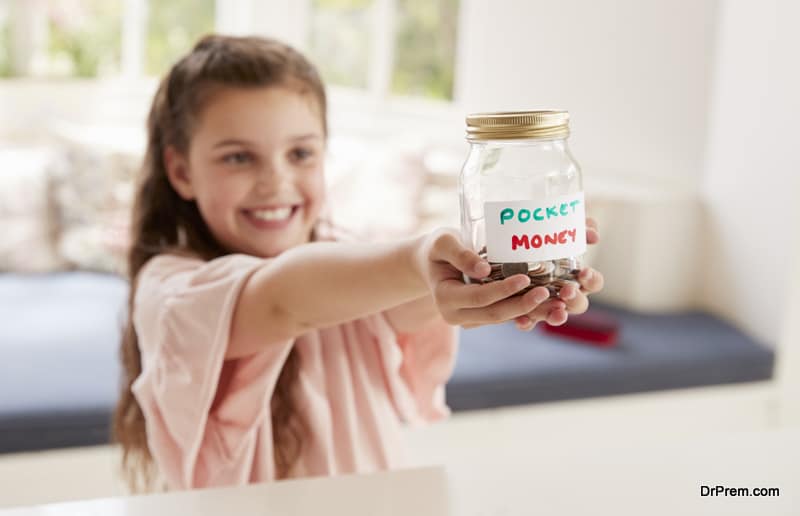 If the stolen thing gets damaged or lost, ask your child to buy it from his pocket money and return it to the concerned person. Once he does this, praise him for this good act.
If the stolen thing gets damaged or lost, ask your child to buy it from his pocket money and return it to the concerned person. Once he does this, praise him for this good act.
4. Try to understand the psychological reasons:
Try to find out the reason behind your kid’s stealing activities. Is he/she in bad company? Is he/she facing some emotional issues at school? Is your child nurturing a grudge on someone? Instead of reacting to your child’s activity, ask the reason. Encourage your child to open up. Your child will feel comfortable and learn to respect your feelings as well.
5. Monitor your child’s behavior:

Try to keep your child away from situations where he/she might be tempted for stealing. If necessary, talk to the school teachers. They will also extend their cooperation in rectifying your child in the most subtle manner.
What if your child continues stealing?
 Even the best tips of how to stop the stealing habit in children may not yield the desired result. Here you should seek professional help as repeated offences might land your child in serious problems.
Even the best tips of how to stop the stealing habit in children may not yield the desired result. Here you should seek professional help as repeated offences might land your child in serious problems.
You can reach out to your family therapist or counselor, school counselor and other support groups (If these are not available in your region, you can opt for medical tourism). Psychologists and counselors normally adopt:
- Behavioral treatments that are focused on specific symptoms. Techniques applied are exposure and response prevention (ERP) and covert sensitization.
- Psychoanalytical treatments focused on underlying psychological reasons. This helps in reducing the symptoms along with improving child’s confidence, self-esteem and coping up skills.
Kleptomania in children is a rare compulsive disorder making up a small percentage of all sorts of compulsive disorders. Once identified, it should be handled properly before the situation goes beyond control transforming the child into a hardened criminal.




