OBESITY AND GASTRO PROCEDURES
TURP | Gall Bladder Removal | Diagnostic laparoscopy | Colonoscopy | Gastric Bypass | Gastric Band Surgery
TURP
TURP AKA Trans Urethral Prostatectomy is a procedure that surgically removes the enlarged portion or section of the prostate gland. The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or enlarged prostate mostly affects aged men.
Why did it need?
TURP is recommended when the patient has symptoms like
- Urine tract infection or acute retention
- Prostate bleeding
- Damage of the kidneys
- Increased frequency of urinating especially at night
- Slow flow or dribbling after urinating
- The patient either has an uncontrollable urge or cannot urinate easily.
Facts and figures
- While 80% of men develop BHP gradually; prostate diseases are more common in men who are 40 and above.
- As per statistics, every year, close to 30,000 men in the United States die due to prostate cancer.
- Amongst the various treatments available for BHP, TURP in today’s world is considered as Gold Standards
- Fabian first described the use of intraprostatic stents during the 1980s. This is one of the secondary treatments to BHP for people suffering from outlet obstruction.
Risk and Complications
- Reaction to medicines or anesthesia
- Blood clots or bleeding
- Breathing problems
- UTI or urine traction infection post-operation
- Tissue scarring
- Damage to adjacent tissues or organs
Advantages
- BHP surgery has a high success rate. Post the surgery, close to 88% of patients have reduced symptoms.
- After the removal of the catheter, most patients will notice their urine flow has improved
- The pain for most patients reduces after the surgery. This makes it easier for them to pass urine and sleep peacefully at night.

Disadvantages
- 10 years post the first surgery, close to 15-20% opt for another one.
- After a TRUP operation, some patients develop fertility issues and temporary problems with urinating.
- In some cases, it has been reported that instead of the semen going out through the urethra, it goes into the bladder.
- Patients tend to develop urethral stricture or transurethral reaction syndrome
Preoperative Preparation
- Complete physical, blood and urine examination
- DRE or Digital examination of the rectal
- PSA or Prostate-specific antigen test
- Physician visit to obtain the list of medicines that have to be stopped or taken before the surgery
- Letting the surgeon know if you drink or smoke
- Arrange for a person to come along with you to drive you back
- Fasting post-midnight before the day of the surgery
- Medical tourists will have to book a hotel room close to the hospital preferably on the ground floor.
Post operative care
- The patient may have to stay back for 1-3 days post the surgery. A catheter will be placed during this time until there are no blood traces found in the urine.
- Post the surgery, the first 6 weeks, a patient will have urination problems or discomfort like pain
Open Prostatectomy
If there is an enlarged prostate that cannot be treated by TURP, then the surgeon would recommend open prostatectomy. This is a surgical procedure that requires a hospital stay and reduces the chances of another surgery. If in the case of prostate cancer, this surgery is contraindicated.
Dos, Don’ts and Precautions
- Good hygiene practices like washing the penis or hands regularly
- Proper rest
- to prevent constipation, laxatives are advisable
- Diet should consist of high fiber foods and lots of fluid
- Post the surgery The patient should not indulge into sexual activity at least for 6 weeks.
- No drinks
- for the first two weeks, it is advisable not to drive
- For 6 weeks, the patient should avoid strenuous activities
- Proper recovery post the surgery will take close to 6-8 weeks
Gall Bladder Removal
Cholecystectomy AKA gallbladder removal is a surgical procedure that is performed to treat gallstones by removing the gallbladder. This can be done by the laparoscopic method which is a less invasive and common method. The other is through an open method.
Why is it needed?
The removal of the gallbladder may be recommended because due to gallstones or because the gallbladder is not functioning as it should. The Symptoms and Signs to watch out for includes
- Severe pain after eating in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Constant feeling of vomiting and nausea
- Indigestion
- Infection
Facts and figures
- Studies have pointed out that in comparison to men women are more prone to develop gallstones. This is especially in the case of overweight or middle-aged women.
- Approximately 10% of people have gallstones
- The removal of the gallbladder is one of the most common salt that many people of for in the Modern Times.
- Carl Johann August Langenbuch a German surgeon developed the gallbladder removal procedure a century ago.
- Dr. Eddi Joe Reddick developed the laparoscopic method in 1989.
Risk and Complications
- Reaction to the medication or anesthesia
- Problem in breathing
- Development of pneumonia post-operation
- Bleeding and/or blood clots
- Infection
- Small intestine or bile duct injury
- Pancreatic inflammation
Advantages
- The removal of the gallbladder helps to improve life quality and provide relief from digestive disturbance.
- If a patient opts for laparoscopic cholecystectomy, he/she does not have to stay in the hospital for a long time.
- Recovery is faster
- After the laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a medical tourist can go back home within a week.

Disadvantages
- Approximately 6% of the patients that opt for laparoscopic surgery may have to go for open surgery. This is because sometimes there are some gall stones that are not completely removed and are still present in the abdominal cavity.
- The most common side effects of laparoscopic surgery are vomiting and nausea.
Preoperative Preparation
- Complete physical, urine and blood examination
- ECG, gallbladder and Chest X-Ray
- Meeting with the specialist to understand what medications are to be stopped or taken before the procedure
- Inform the surgeon about alcohol or smoking habits or even pregnancy planning
- Counseling for a diet change and nutritional factors
- Making necessary arrangements for help post the surgery
- Post midnight before the surgery, the patient should not eat or drink anything.
- It is advisable that medical tourists book a room that has handicapped access and is close to the hospital.
Post operative care
- Post the laparoscopic surgery, a patient can go home the same day. In the case of open surgery, the patient will be discharged 5-7 days post the surgery.
- If a patient undergoes opens surgery, they will be under observation for a day. The hospital staff will provide all the help needed
- Initially, the patient will be on IV fluids, gradually he/she will move to a liquid diet and eventually a solid diet. Medications will be given to prevent reduce abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or nausea
Precautions and Preventive measures post the surgery
- The patient will have to follow a particular diet post the surgery
- The patient should avoid strenuous activities, lifting heavy things, or drive for 2-3 days.
Diagnostic laparoscopy
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a surgical procedure, which allows a doctor to have a look at the pelvis or abdomen. This procedure is conducted to diagnose infection and infertility issues. Trough this procedure, the doctor can check out organs like the large and small bowel, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes and even the gallbladder and liver
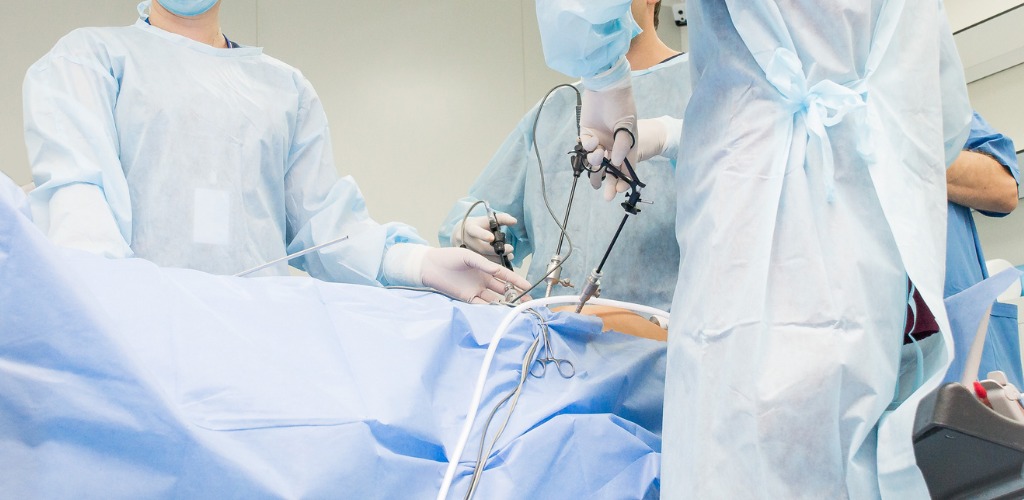
Risk and complication
- Although considered a safe procedure; it is very rare that a patient may develop any complication after a diagnostic laparoscopy due to factors like
- Infection and/or bleeding
- Abdominal discomfort and cramps
- Puncture of adjacent organ

Uses of the procedure
- The diagnostic laparoscopy is recommended to diagnose and detect conditions like
- Appendicitis
- Gallbladder inflammation
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic
- Evaluation of abdomen organ injuries
Preparation for the procedure
- 8 hours fasting before the procedure is advisable
- The doctor should be informed of any allergies beforehand
- Remove jewelry and dress up comfortably for the procedure
- Take someone along with you to drive you back after the procedure
During the Procedure
- The diagnostic laparoscopy may or may not require the patient to be admitted depending on the case in question.
- Local or general anesthesia would be used based on the specialist’s decision.
- To have a proper view of the internal organs, a small cut will be made on the abdomen to insert the laparoscope.
- If additional surgical tools have to be inserted the surgeon may make additional incisions.
- Once the entire procedure is completed, the doctor will not only take out all the tools and laparoscope; however, he/she will also cover the incisions.
- Certain medications will be prescribed for controlling the pain and preventing infection.
Travelers guide
- For faster recovery post-procedure, it is advisable to book a room on the ground floor( in case there is no lift) at a hotel close to the hospital.
- If the procedure is in your home city, you can go back home after the procedure. However, as a medical tourist, you would need to stay back for a day or two for recovery.
- If needed, a second opinion can be taken with a specialist before the procedure or as a follow-up afterward.
- After the procedure, it is advisable not to drive for at least 24 hours. A patient can resume back to work after three days.
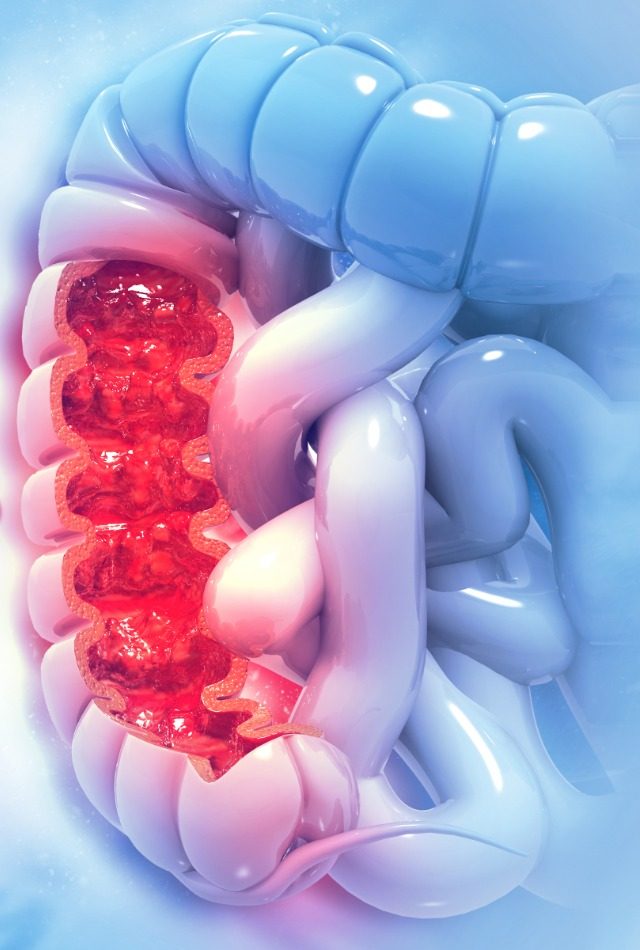
Colonoscopy
The Colonoscopy is performed to examine and view the rectum and colon. This procedure helps to treat intestinal problems like colon cancer or inflammatory diseases.
Uses of the colonoscopy
- As a screening test for early detection of colorectal cancer and taking a biopsy sample if needed
- Removal of polyp
- Evaluating the symptoms of certain inflammatory bowel diseases due to rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, a sudden change in bowel habits and non-dietary weight loss

Risk and Complications
- Although it is very rare, complications may develop if there is a removal of a polyp.
- Some of the other complications could be due to a reaction to the medication, bleeding, and perforation.
Preparations for the procedure
- A day or two before the procedure, the patient will be put on a liquid diet. This is called bowel preparation. The patient may also be given an enema to prepare the bowel for the procedure.
- Before the procedure, the patient will be advised to keep 8-10 hours of the gap from the last meal.
- It would be advisable to get someone along with you to drive you home after the procedure.
During the procedure
- A Colonoscopy generally lasts between 30-60 minutes and does not require admission in the hospital
- The patient would have to change into an examination gown and lay down on the left side with knees bent.
- Pain medications and sedatives will be given to the patient via IV through the arm.
- For proper guidance, the surgeon will use the colonoscope by inserting it into the rectum. This flexible and long instrument, ½” in diameter and is equipped with a fiber-optic camera.
- Small growths and tissue samples will be collected/removed with the help of special tools/attachment
- The patient can go home after the sedation wears off.
- He or she may experience cramping, flatulence, or even slight bleeding after the procedure.
Travelers guide
- Medical tourists would have to undergo bowel preparations a day or two before the procedure
- Tourists can go back home after full recovery
- Patients should not drive for 24 hours due to the effects of the sedation
Gastric Bypass
Definition:
Gastric bypass is the surgical procedure for obesity treatment. This involves creating a stomach pouch that restricts food intake. Small intestine is attached directly to new stomach pouch, bypassing the lower stomach and duodenum.
The patient eats less after surgery as he/she feels full sooner, leading to loss of weight. Surgery is possible via Laparoscope Open Incision
The patient eats less after surgery as he/she feels full sooner, leading to loss of weight. Surgery is possible via Laparoscope Open Incision
Why is it needed?
This surgery is prescribed when obese patients cannot lose weight by other methods.
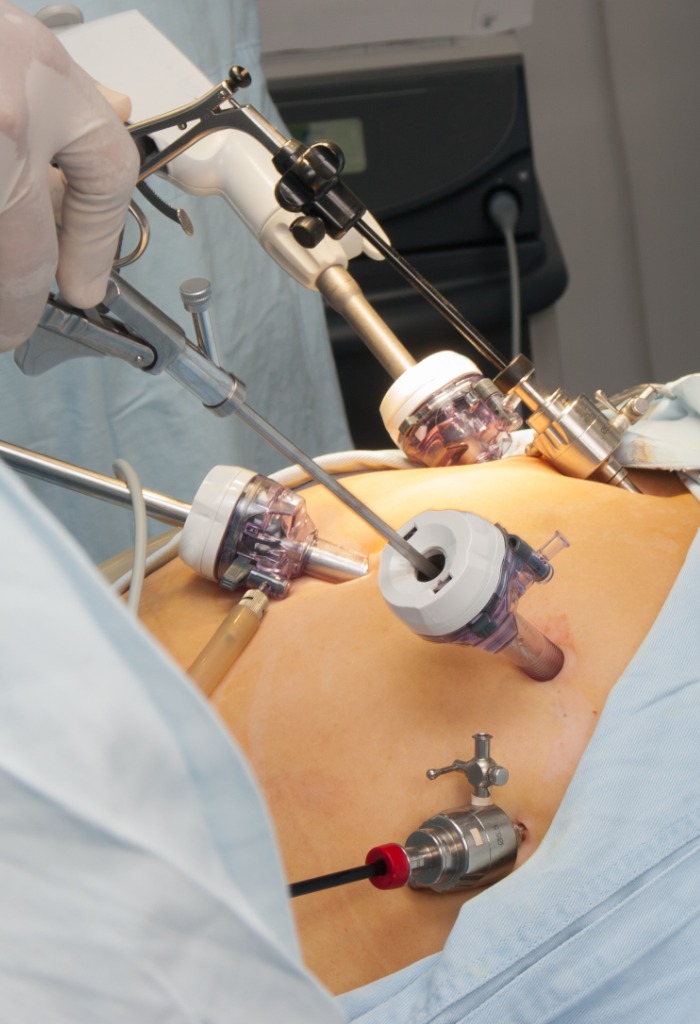
The ideal candidate for surgery:
- BMI -body mass index equal to 40 or more
- Those whose BMI is 35 or more, but suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes, sleep apnoea, osteoarthritis, heart disease and so on, and would benefit from weight loss
- Aged between 18 -55 years and willing to followed prescribed diet (and restrictions)
Facts and figures
- Obesity causes premature deaths worldwide. It is ranked second in the cause of preventable deaths in US, where it causes 300,000 deaths every year.
- Linner and Kremen performed the first surgery, which led to the modern method of bariatric surgery
Risk and Complications
- Reaction to medication or anesthesia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Blood clots
- Pneumonia
- Bleeding
- Injuries to the intestine, stomach, or adjacent organ/s
- Dumping syndrome
Advantages
- Marked weight reduction after surgery. It makes life comfortable as patients as it eases daily activities and movement.
- Definite improvement is observed in medical conditions such as asthma, hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnoea etc.
Disadvantages
- Surgery may increase chance of developing gall bladder stones.
- A chance for developing Hernia.
- Malnutrition may occur leading to Osteoporosis, Anemia, and/ or Depression.
- Leaking via the staples in stomach post-surgery may need emergency surgery
Preoperative Preparation
- Full-body physical examination
- Blood plus urinalysis
- Ultrasound – abdomen
- Visiting surgeon to have a list of medicines for pre and post-surgery
- Inform surgeon about alcohol or smoking habits
- Nutritional counseling
- Receiving counseling for mental health, to cope with emotional and physical changes post surgery
- Arrange work leave, help at home and driving, and post-operative care
- Fasting after midnight before surgery
- Medical tourist should select a handicapped-accessible hotel near hospital post-surgery recuperation
Postoperative Preparation
- Patients have stay for 3-5 days in hospital post-surgery. The catheter is used to drain body fluids, which is removed within 1-3 days post-surgery
- Pain medication is given
- Patients have to ingest liquids for 1-3 days, then soft food is allowed
Dos, Don’ts and Precautions
- Do eat small amounts at one go
- Avoid foods having simple sugars like juice, candy, juice, beverages, condiments, soft drinks to avoid ‘Dumping syndrome’
- Do follow diet prescribed strictly. Exercise regularly to receive best outcome of surgery
Gastric Band Surgery
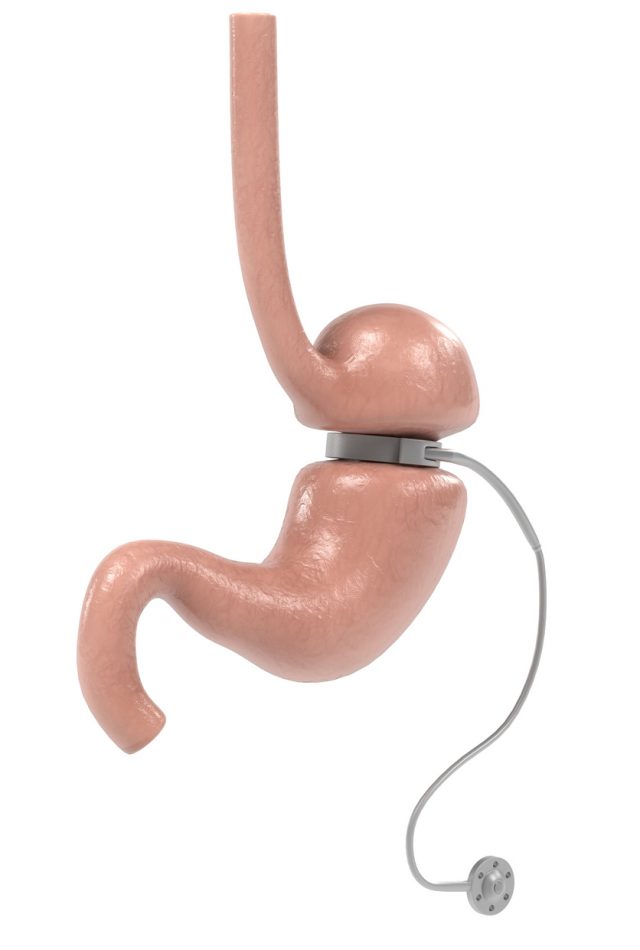
- Definition: This surgery is commonly performed as a treatment for obesity. In this, an adjustable silicon band is placed around the upper part of the patient’s stomach, via a laparascope. This reduces the stomach’s volume which limits the food amount which can be consumed at one sitting. It also makes the patient feel full quickly.
- The two FDA approved bands are
- Lap-Band
- Realize Band
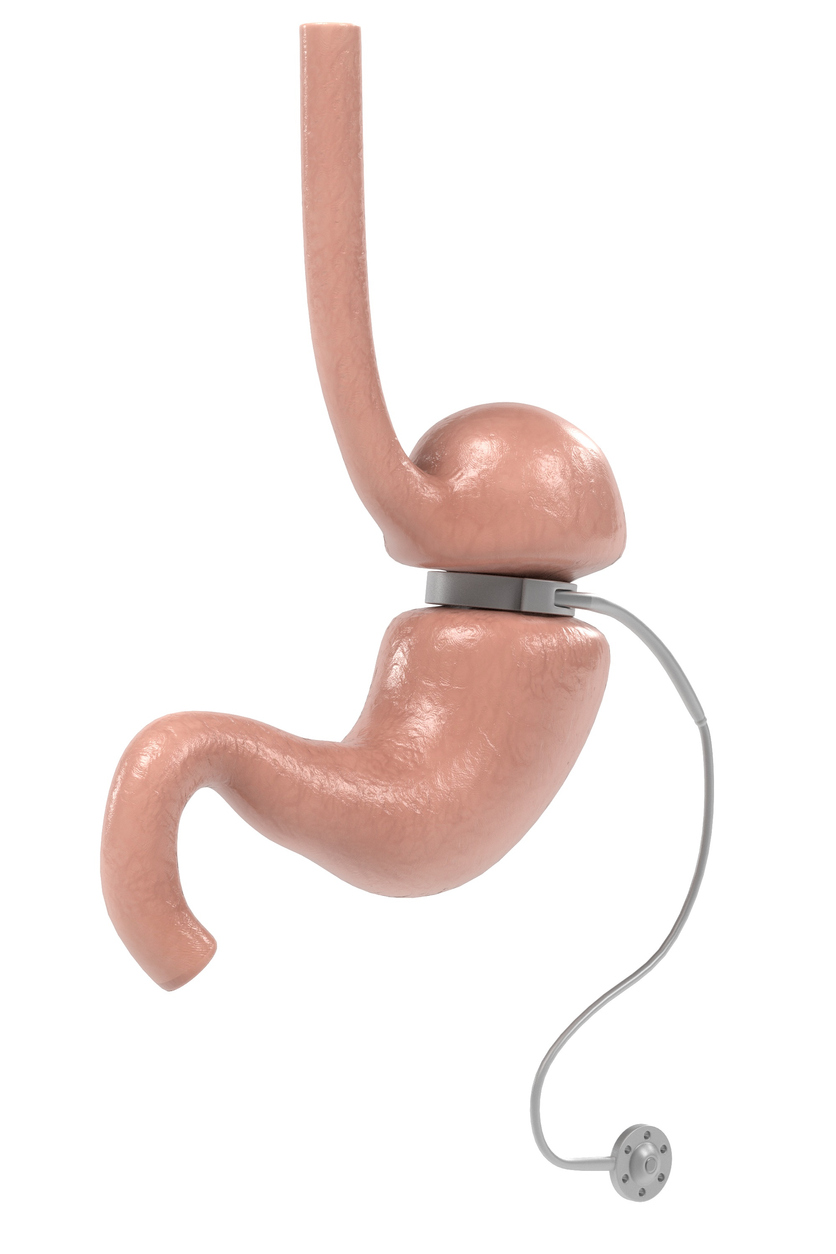
Why is it needed?
- This bariatric surgery gastric band is meant for obese patients who are unable to lose their weight through exercise and diet. The ideal candidate for this surgery are:
- Those who have BMI (body mass index) equal to 40 or higher
- Those whose BMI is 35 but suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, heart disease and so on, and would benefit from weight loss
- Aged between 18 -55 years and willing to followed prescribed diet (and restrictions)
Facts and Figures
Reaction to medication or anesthesia
- Blood clots
- Pulmonary embolism
- Infection
- Abdominal organs’ injury
- Gastric band slippage
- Gastritis or stomach ulcer
- Bowel obstruction
Advantages
- Brain tumor removal surgery which is successful, saves and extends patient life
- Patients get relief from symptoms and can continue to live with improved quality of life
- A surgeon named William, was the first surgeon to remove brain tumor in 1879

Disadvantages
- Sometimes, surgery on a particular part/area of the bone can cause the loss of some mental functions such as – speech related disorders, memory, muscle weakness, imbalance, coordination, vision and so on. These disorders can last for a short or long duration, and sometimes, never go away
- Chance to develop fatal brain herniation
Preoperative Preparation
- Physical examination
- Urinalysis and Blood test
- Ultrasound-abdomen, X-ray- chest
- Get list of medicines to be taken pre and post-surgery
- Inform surgeon about alcohol or smoking habits
- Nutritional counseling
- Arrange work leave, help at home and driving, and post-operative care
- Fasting after midnight before surgery
- Medical tourists should select a hotel near the hospital
Post operative care
- Constipation after surgery which subsides after some days
- Patients must walk slowly after they reach home
- Do’s, Don’ts, and Precautions:
- Take surgeon prescribed medicines
- Keep incision site dry and clean
- Avoid being pregnant for a minimum 18 months post-surgery
- Avoid using straws
- Avoid drinking carbonated beverages
- Maintain food intake diary and record weight loss post-surgery
- Do strictly follow the diet regime prescribed
- No driving until permitted by a doctor