ONCOLOGY

DR PREM MEDICAL TOURISM ADVISOR AND FACILITATOR SUPPORT - WORLD's #1 ADVISOR
We are World’s Best and #1 Medical Tourism Advisor. We Provide Comprehensive Supports, Solutions, Guidance, Training, Knowledge, Patient Management Tools, Online Records, Telemedicine to Patients and Facilitators to get the best posible treatments from world’s leading hospital with Quality, Care, Saving and Unmatched Services.
Find Best Healthcare Provider
Find Top Medical Tourism in India
Medical Tourism Support Services
Free Telemedicine and Free Consultation
Connect with Top Dr Prem Medical Tourism Advisor and Facilitator
Ethical, Cultural and Legal Medical Tourism Services
Free Consultation
Dr Prem Offers medical tourist the benefit of the free consultation before trip.
Affordable Packages
Our clients gets benefit of saving money as they get customised package.
Visa Process
Visa process is important if you want to travel any other countries. For Medical tourist there is a special medical visa.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is the ability to provide interactive healthcare support via modern technology and telecommunications. It enables the patient to receive Pre Operative or Post Operative treatment without spending much money.

Travel Arrangement
Making travel arrangement is very confusing specially in case of medical tourist.
Accommodation
Dr Prem will also ensure that we help you making necessary arrangement for staying.
Translation Services
For those who are not fluent in english it can be very difficult to communicate especially if you are out of home country
Medical Matchmaking
Dr Prem Medical tourism matchmaking is world’s leading AI driven tool, it involves identifying the right services matching the requirements and objectives of a medical traveler in terms of cost, quality and processing time.
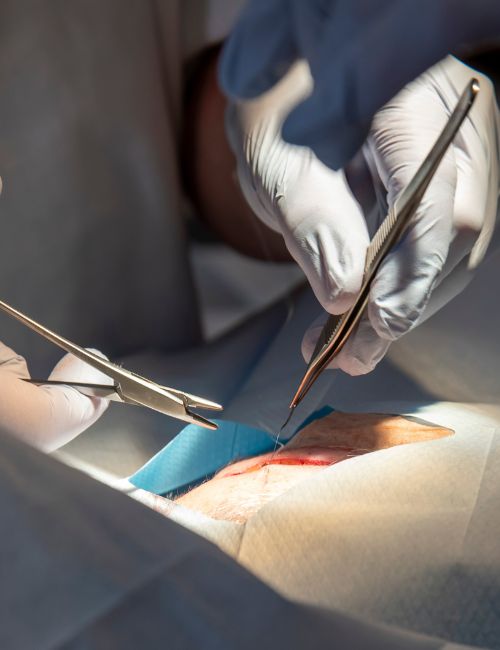
Cancer Surgery

Procedure in a Nutshell:
The procedure involves making an incision in the body to access the cancerous tumor or tissue.
The tumor or tissue is then removed, along with some surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all cancerous cells have been removed.
Depending on the location and size of the tumor, the surgery may be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic surgery.
Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Cancer surgery is one of the most common treatments for cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, over 1.8 million people in the United States will be diagnosed with cancer in 2022, and many of them will require surgery.
The success of cancer surgery depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer, and the patient’s overall health.
Risks and Complications:
As with any surgery, there are risks and complications associated with cancer surgery, including bleeding, infection, blood clots, and damage to surrounding tissues and organs.
In some cases, cancer surgery may lead to long-term side effects, such as lymphedema (swelling caused by the removal of lymph nodes) or nerve damage.
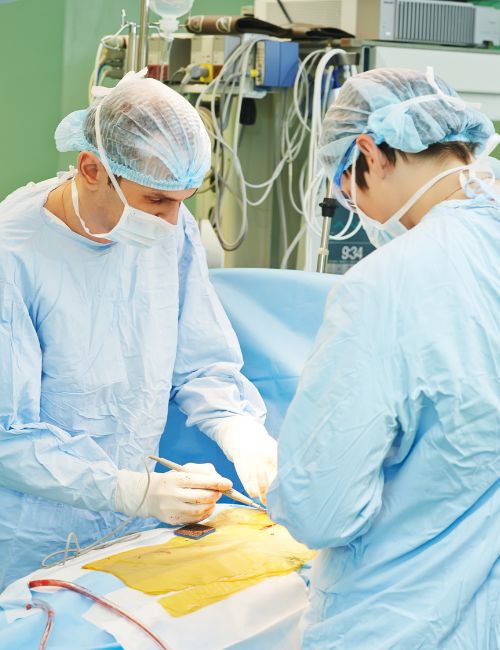
Post Operative Preparation:
After the surgery, the patient will be monitored closely for any signs of complications, such as bleeding or infection.
Pain medication and other supportive therapies may be provided to help manage any discomfort or side effects.
In some cases, the patient may require rehabilitation or physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
Preoperative Preparation:
Before the surgery, the patient will undergo a thorough medical evaluation to determine if they are healthy enough for surgery.
Depending on the type of cancer and the patient’s overall health, they may be asked to stop taking certain medications or to change their diet in the days leading up to the surgery.

Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
It is important for the patient to follow their doctor’s instructions carefully and to avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting for several weeks after the surgery.
Depending on the location of the surgery, the patient may need to avoid certain movements or activities until they have fully healed.
It is important for the patient to attend all follow-up appointments and to report any unusual symptoms or side effects to their doctor.
Radiation therapy
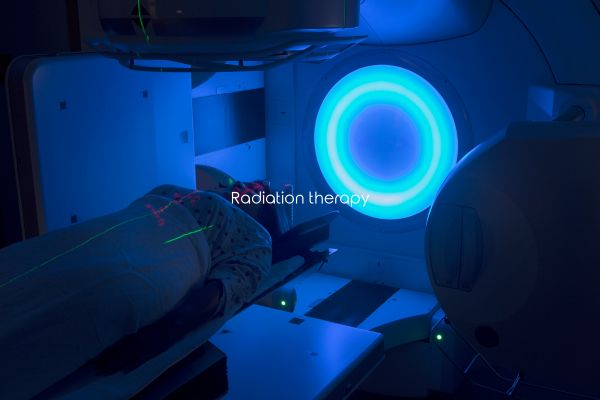
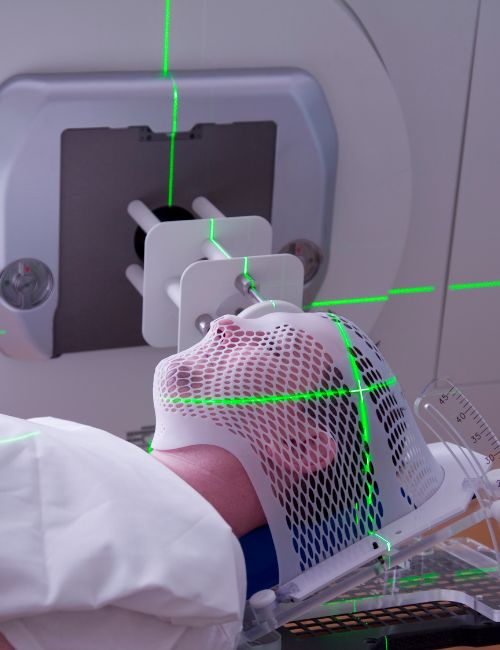
Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Radiation therapy is one of the most common treatments for cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, over half of all cancer patients receive radiation therapy at some point during their treatment.
The success of radiation therapy depends on several factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, the location of the cancer, and the patient’s overall health.
Risks and Complications:
Like all medical procedures, radiation therapy has some risks and potential complications.
Common side effects of radiation therapy include fatigue, skin irritation, nausea, and hair loss.
In rare cases, radiation therapy may cause long-term side effects, such as organ damage or an increased risk of developing a second cancer.
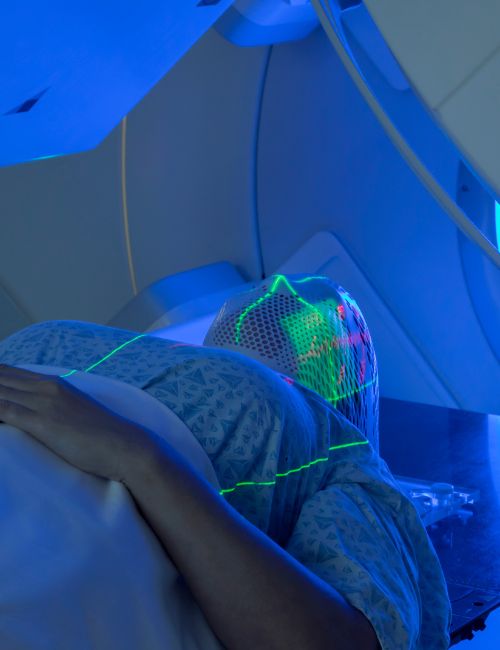
Post Operative Preparation:
Preoperative Preparation:
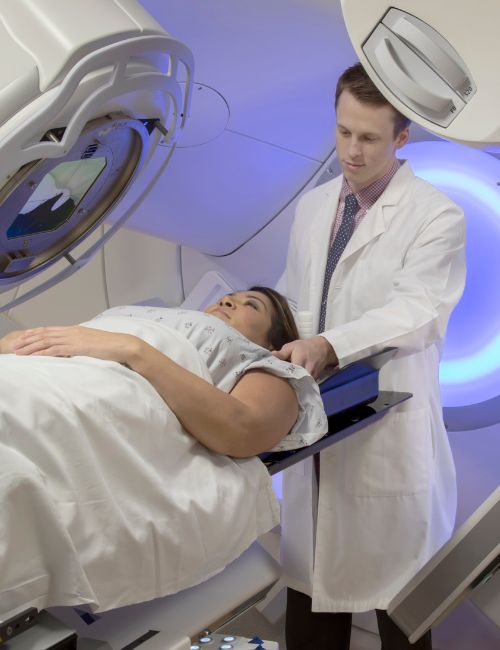
Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
During radiation therapy, the patient should avoid exposing the treated area to the sun or extreme temperatures.
The patient should also avoid using any lotions, creams, or other products on the treated area without first consulting their doctor.
It is important for the patient to attend all follow-up appointments and to report any unusual symptoms or side effects to their doctor.
Chemotherapy
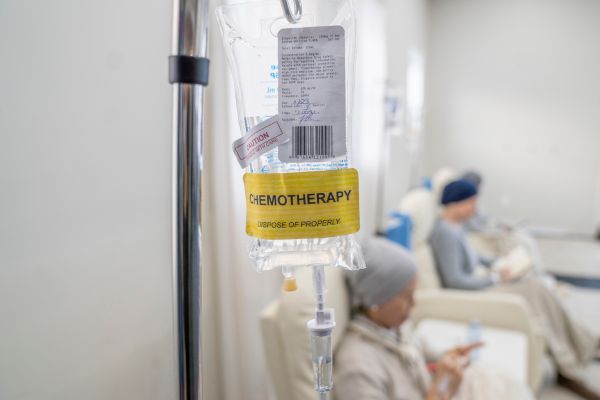
Procedure in a Nutshell:
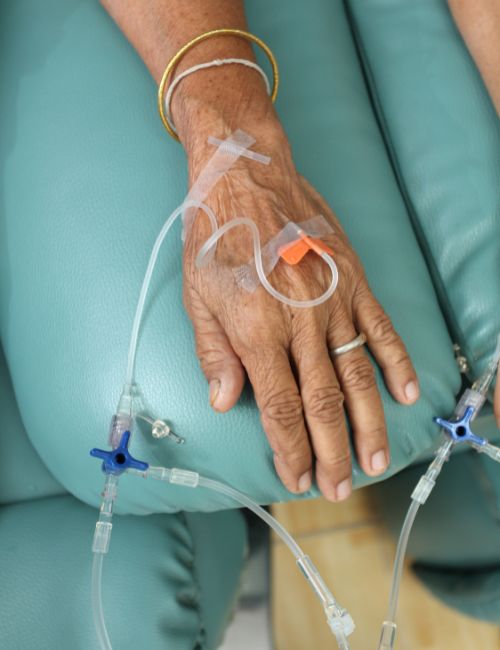
Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Risks and Complications:

Post Operative Preparation:
Preoperative Preparation:
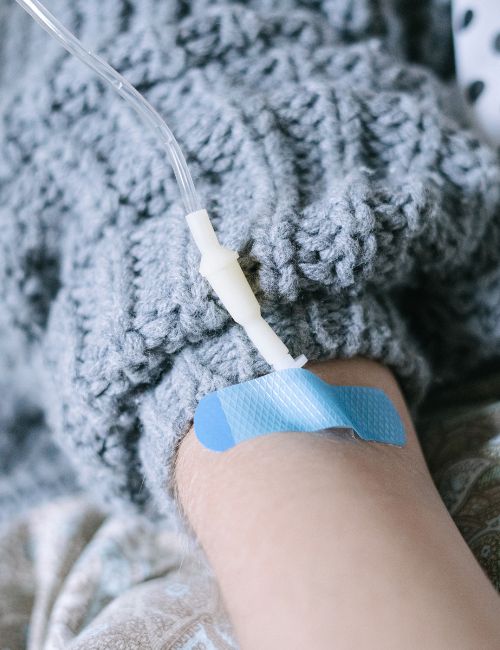
Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
Immunotherapy
Procedure in a Nutshell:
Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Risks and Complications:
Post Operative Preparation:
Preoperative Preparation:

Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
Targeted Therapy

Procedure in a Nutshell:

Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Risks and Complications:

Post Operative Preparation:
Preoperative Preparation:

Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
Hormone Therapy

Procedure in a Nutshell:
Why is it needed?
Facts and Figures:
Risks and Complications:
Post Operative Preparation:
Preoperative Preparation:
Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
Precision Oncology
Precision Oncology is a type of cancer treatment that uses genetic testing and other advanced techniques to tailor treatment to an individual’s specific genetic makeup and other unique characteristics.

Procedure in a Nutshell:
Precision oncology for cancer treatment involves several steps, including genetic testing to identify specific mutations or other abnormalities that are driving the cancer’s growth, and the use of targeted therapies or immunotherapies that are designed to specifically target these abnormalities.
Other advanced techniques, such as liquid biopsy and next-generation sequencing, may also be used to help identify potential targets for treatment.
Why is it needed?
Precision oncology is needed because not all cancers are the same, and traditional treatments such as chemotherapy may not be effective for all patients.
By identifying the specific genetic mutations or other abnormalities that are driving the cancer’s growth, precision medicine can help identify treatments that are more likely to be effective, while minimizing side effects and other risks associated with traditional treatments.
Facts and Figures:
Precision oncology is a rapidly evolving field, and new treatments and techniques are being developed all the time.
According to the Precision oncology Initiative, precision oncology has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment, leading to more targeted and effective treatments, improved outcomes, and fewer side effects.
Risks and Complications:
Like other types of cancer treatment, precision oncology carries some risks and complications, including potential side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.
Some targeted therapies may also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or heart problems.
Do's, Don'ts and Precautions:
The patient should inform their healthcare provider of any symptoms or side effects they experience, as prompt medical attention may be necessary.
The patient should also inform their healthcare provider of any other medications or supplements they are taking, as these may interact with precision oncology treatments.
The patient should also maintain good self-care practices, such as getting enough rest and exercise, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking and other unhealthy habits.