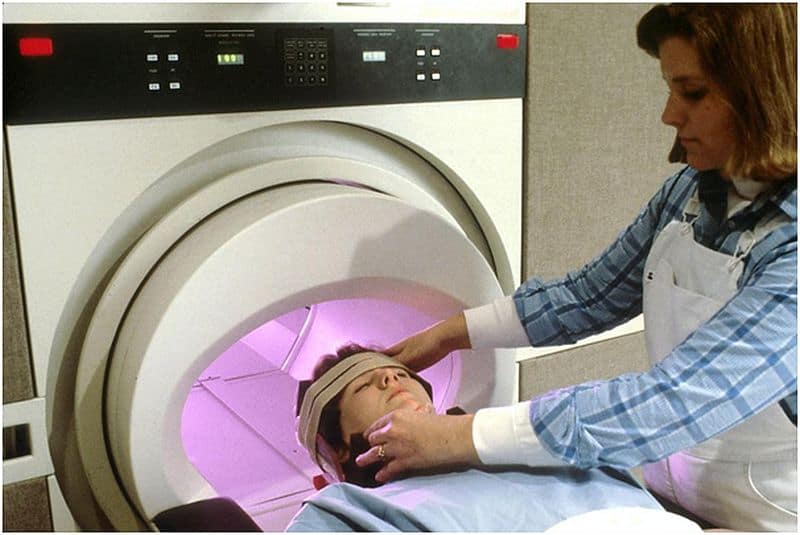
In the constantly changing landscape of medical technology, magnetic resonance imaging is a product of cutting-edge advancement. This non-intrusive method of imaging has not only transformed how we see the inner workings of the human body but also reshaped the core of medical investigation. Within the healthcare industry, it’s a vital instrument, with over 30 million scans performed every year.
Contrary to conventional methods like X-rays and CT scans, which depend on ionizing radiation, MRI functions in a wholly unique way. Utilizing a complex combination of magnetic fields and radio waves, MRI crafts intricate and accurate depictions of the body’s inner structures. This technique is carried out without any physical penetration or exposure to possibly dangerous radiation, providing a more secure and refined understanding of human anatomy.
In a nutshell, MRI technology represents a sophisticated integration of scientific principles and innovative design. It serves as a window into the human body, providing unparalleled insights into the hidden complexities of our internal structures.
In this article, we will embark on an exploration of the multifaceted world of MRI. We will delve into the underlying science that drives this remarkable technology, examine its diverse applications in gastrointestinal health, and consider the exciting future innovations on the horizon.
The Science Behind MRI: Unveiling the Value of Precision Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging stands as a pinnacle of innovation when it comes to medical imaging solutions, offering unparalleled insights into the human body. Beyond its technical complexity, the true value of MRI lies in its ability to transform healthcare through precise diagnosis, targeted treatment, and patient-centered care. Let’s explore the scientific foundations of MRI and uncover the value it brings to modern medicine.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): A Scientific Marvel
MRI operates on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), a phenomenon where atomic nuclei respond to a magnetic field. The human body, rich in water molecules, becomes a canvas for MRI, as the hydrogen atoms within align with the magnetic field. This alignment sets the stage for a process that transcends mere imaging, opening doors to medical breakthroughs and personalized care.
How MRI Works: A Process of Precision
- Magnetic alignment: The alignment of hydrogen atoms with the magnetic field is not just a scientific curiosity; it’s the first step in creating images that can detect diseases early, monitor treatment progress, and guide surgical interventions.
- Radiofrequency pulses: Controlled radio waves cause the atoms to resonate, a process that translates into detailed images. These images are more than visual representations; they are tools that empower physicians to make informed decisions, enhancing patient outcomes.
- Signal detection: The MRI machine’s ability to detect signals from resonating atoms is a testament to technological advancement. It reflects a commitment to accuracy and quality, ensuring that the images produced are reliable and actionable.
- Image formation: The transformation of signals into images is a fusion of science and art. The resulting images provide a window into the body’s hidden landscapes, enabling personalized treatment plans, reducing unnecessary procedures, and improving the overall patient experience.
Applications of MRI in Gastrointestinal (GI) Health: A New Horizon of Care
The field of gastrointestinal health stands at the forefront of medical innovation, and magnetic resonance imaging plays a pivotal role in this transformation. The applications of MRI in GI health extend beyond mere imaging; they represent a paradigm shift in research, diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. Let’s explore the multifaceted impact of MRI on GI health.
1. Early Diagnosis and Prevention
MRI’s ability to provide detailed images of soft tissues makes it an invaluable tool for early diagnosis of GI disorders. From detecting inflammation to identifying tumors, MRI offers a non-invasive pathway to uncovering conditions that might otherwise remain hidden.
This early intervention can lead to more effective treatment and even prevention of more serious complications.
2. Guiding Treatment and Intervention
In the complex landscape of GI health, precision is paramount. MRI not only aids in diagnosis but also guides therapeutic interventions. Whether planning a surgical procedure or monitoring the response to medication, MRI provides real-time insights that enhance decision-making and patient outcomes.
3. Research and Drug Development
The applications of MRI in GI health extend into the realm of research and drug development. By offering a window into the body’s response to new treatments, MRI accelerates the path from laboratory discovery to clinical application.
It’s a bridge between scientific curiosity and life-saving innovation.
The Topic of Superconductivity
MRI stands at the forefront of innovation, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. The most recent advancement is one of the most exciting prospects: the potential integration of room-temperature superconductivity, with particular attention to the current claims surrounding a compound known as LK-99.
This could mark a transformative era for MRI technology, redefining medical imaging and unlocking new horizons in patient care.
The Potential of LK-99: A Closer Look
- Superconducting properties: In order to operate correctly, MRI machines require superconducting materials to generate the strong magnetic fields necessary for imaging. Traditional superconducting materials used in MRI must be cooled to extremely low temperatures, near absolute zero, to maintain their superconducting state. This cooling is typically achieved using liquid helium, a process that is both energy-intensive and expensive.
LK-99 is a material claimed to act as a superconductor at room temperature and even at temperatures as high as 127°C. The implications of this claim are profound; if validated, it could revolutionize MRI technology by significantly reducing or entirely eliminating the need for extreme cooling that current superconducting materials require.
This advancement could pave the way for more energy-efficient and cost-effective MRI machines, potentially transforming the accessibility and sustainability of medical imaging technology.
- Structure and synthesis: The unique structure of LK-99, akin to lead‒apatite with trace copper, opens doors for exploration and development. Understanding its synthesis could lead to new materials and technologies, fostering innovation in the medical field.
- Scientific scrutiny: LK-99’s claims have stirred both interest and skepticism. Rigorous examination and validation are essential, with collaborative research and transparent communication setting the stage for potential breakthroughs in medical technology.
Implications for MRI Technology
The integration of room-temperature superconductivity into MRI technology is not merely a technical advancement; it’s a pathway to a new era of healthcare. Enhanced MRI machines could provide more detailed images, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. This precision translates into more informed decisions, tailored treatments, and enhanced patient care.
The potential reduction in operational costs could democratize MRI, making it accessible to a broader population. It’s a step towards healthcare equity, ensuring that this vital tool is within reach for more individuals.
Aligning with global sustainability goals, the environmental impact of superconductivity in MRI reflects a responsible approach to technological advancement. It’s a commitment to a greener future, harmonizing medical innovation with ecological responsibility.
Furthermore, exploring room-temperature superconductivity fosters collaboration between various scientific disciplines, bridging gaps and igniting a collective pursuit of excellence.
All in all, It’s a multidisciplinary approach that fuels innovation and reflects the interconnected nature of modern science, poised to usher in a new era of healthcare.
Article Submitted By Community Writer