Rheumatology
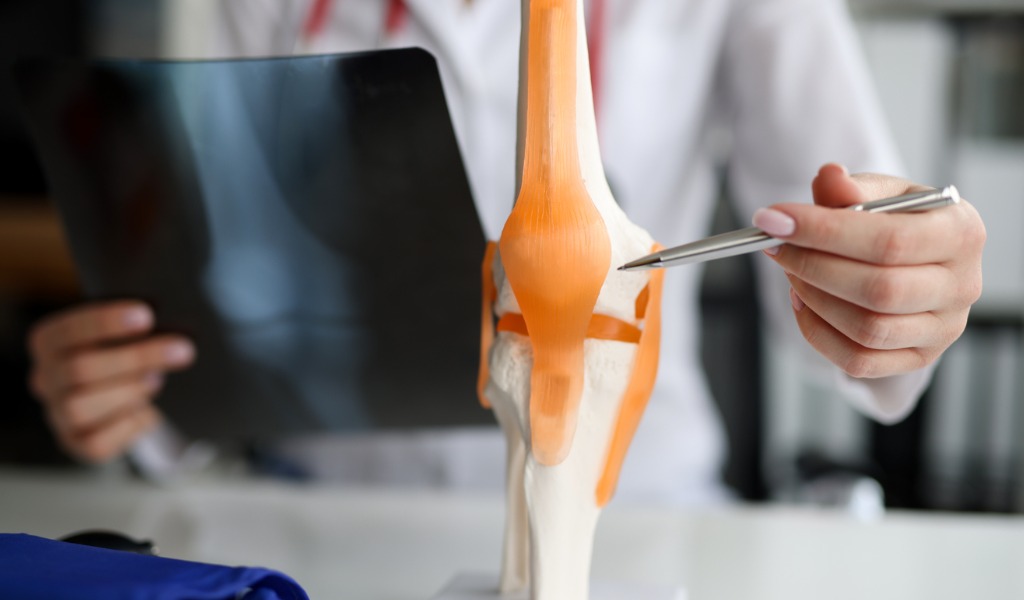
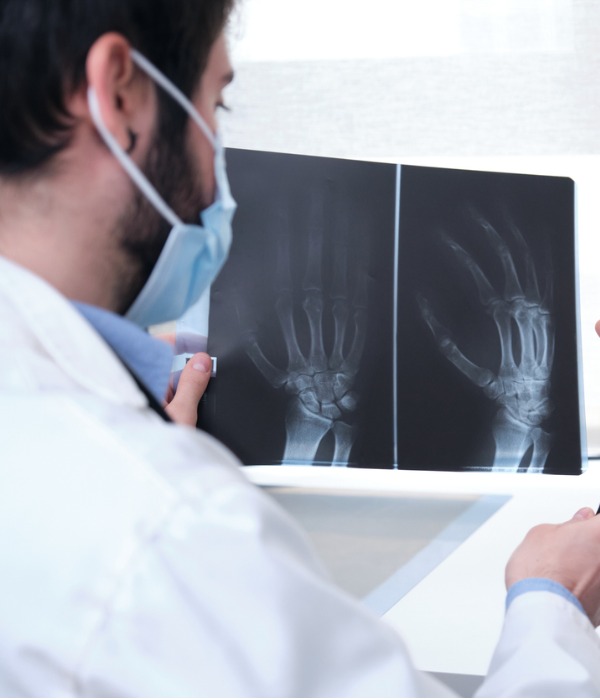
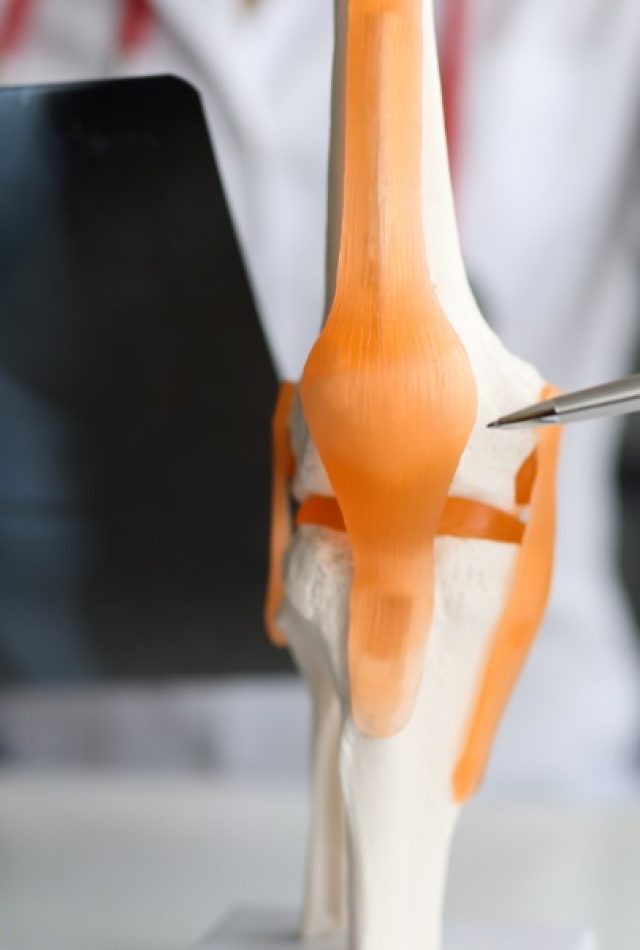
- Definition: Rheumatology is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis a well as therapy of the immune system disorders
- Rheumatologists deal with the immune related disorders of musculoskeletal system,, autoimmune diseases, soft tissues, vasculitis’s, and some inherited connective tissue disorders